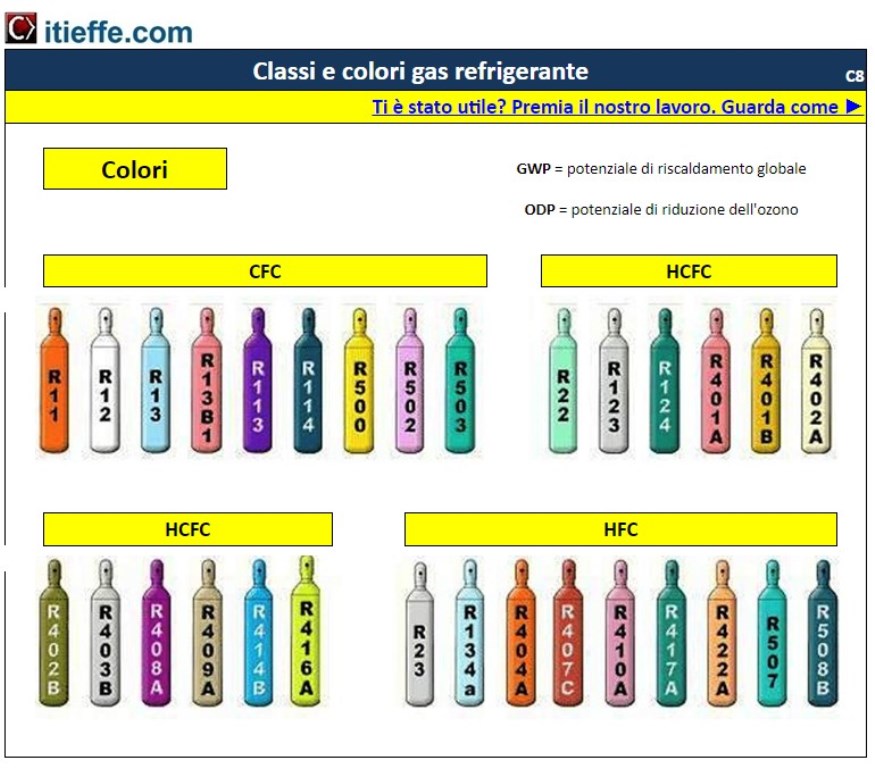
Indications of the standardized colors used on the most commonly used refrigerant gas containers and on the differentiation classes (CFC - HCFC - HFC - HFO) ordered according to damage to the ozone layer (ODP) and global warming potential (GWP)
We are pleased to present this informative guide on standardized colors for refrigerant gas containers, an important resource for professionals and enthusiasts in the cooling and air conditioning industry. This publication, produced by Itieffe, is designed to provide a useful overview of the different classes of refrigerant gases, including chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and hydrofluorolefins (HFOs), as well as to discuss their depletion of the ozone layer (ODP) and their global warming potential (GWP).
Refrigeration and air conditioning industry
Over the past few decades, the refrigeration and air conditioning industry has undergone significant changes, driven by ever-increasing environmental concerns and the need to reduce negative impacts on the environment. This guide is an attempt to simplify the complex landscape of refrigerant gases by offering a standardized color system for refrigerant gas containers, which can facilitate the safe handling and identification of refrigerants.
The heart of this guide is the classification of refrigerant gases based on their potential environmental impact, with particular attention to two crucial parameters: their ODP (Detriment to the ozone layer) and GWP (Global Warming Potential). Each class of refrigerant gas is associated with a specific color, which should be used to label containers, thus making it easier to distinguish between different categories of refrigerants.
It is crucial for everyone who works with refrigerant gases to understand the importance of choosing and using refrigerants responsibly. The guide also covers regulatory developments and measures adopted internationally to limit the use of high-GWP and ozone-depleting refrigerant gases, encouraging the adoption of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
This guide was prepared with the aim of being a clear and practical resource for anyone involved in the refrigerant gas industry, from service technicians to cooling system designers, from HVACR operators to environmental policy makers.
We are confident that this guide will help improve awareness and responsible management of refrigerant gases, promoting a healthier and more sustainable environment for all of us and for future generations.
Classes and colors of refrigerant gas
Indications of the standardized colors used on the most commonly used refrigerant gas containers and on the differentiation classes (CFC - HCFC - HFC - HFO) ordered according to damage to the ozone layer (ODP) and global warming potential (GWP)
The ODP coefficient
In recent years, awareness of environmental issues has led, especially in Europe, to the introduction of increasingly severe and eco-friendly legislation.
Due to their increasingly global diffusion, air conditioning systems have passed under the magnifying glass of the European Union, which has regulated their use, with the aim of minimizing the impact and risks for the environment.
One of the most used parameters is undoubtedly the Ozon Depletion Potential, or ODP, which serves to indicate how much the use of a chemical compound can damage and consume the ozone present in the earth's atmosphere, indirectly contributing to the phenomenon of 'greenhouse effect.
However, it is good to know that ODP alone cannot estimate the potential effect a gas can have on the greenhouse effect. To estimate this potential it will be necessary to use another parameter, namely the Global Warming Potential, or GWP.
The GWP parameter
The acronym GWP indicates the Global Warming Potential, or the global warming potential. This parameter is calculated for each greenhouse gas, in a very complex way. Simplifying, we could say that the GWP is calculated as a weighted sum of the contributions to the greenhouse effect of each molecule of which the gas is made, in a relative way with respect to CO2. Basically, each molecule of which the gas is made will have an impact factor (IF), which will be related to that of carbon dioxide. The latter, being taken as a unit of measurement, will have IF equal to 1.
Furthermore, the GWP can be calculated on the basis of long or short term impact. In general, there are many GWPs, based on the time interval over which they are calculated. For example, GWP20, GWP50 and GWP100 will indicate, respectively, the impact on the greenhouse effect at 20, 50 and 100 years.

"Eco friendly" Cooling Fluids
R 32 refrigerant is an HFC used as a component of refrigerant mixtures for low temperature applications. The flammability characteristics of the R 32 refrigerant allow it to be used only in new systems, specifically designed for the R 32 refrigerant.
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
Classes and colors of refrigerant gas
The program / paper shown below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
If you want, you can sign up now by clicking HERE
