Calculation of winter heat requirements
Calculation of the winter heating requirements needed to heat a room and the sizing of the necessary radiant elements in aluminum and cast iron.
This is a free program created and offered by Itieffe, dedicated to calculating winter heating needs and determining the number and size of radiators needed, it is an essential tool in the field of energy efficiency and thermal comfort in buildings. This type of software offers a systematic and accurate approach to address two fundamental aspects in the field of heating systems: quantifying the amount of energy needed to heat a room during the winter season and sizing the radiators so as to distribute the heat evenly necessary within them (it does not however replace the work of the heating engineer).
In a context where environmental sustainability and energy efficiency are increasingly important, a program of this type plays a crucial role. The calculation of the winter heating requirement makes it possible to optimize the use of energy resources, avoiding energy waste and contributing to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. This is especially important in a world where reducing environmental impact is a priority.
Furthermore, determining the number and size of aluminum and cast iron radiators accurately is essential to ensure the thermal comfort of a building's occupants. A well-designed and appropriately sized heating system ensures that rooms are heated evenly and that there are no unwanted cold or hot spots. This not only increases comfort, but can also improve productivity and occupant health.
Dedicated program
The availability of a dedicated program greatly simplifies the design and implementation process calculation, reducing the margin of human error and allowing to take into account a series of complex variables, such as thermal insulation, geographical location, heat losses and other specific conditions of the building.
In summary, a program that calculates winter heating requirements and sizes radiators is a fundamental tool for designing efficient and effective heating systems. It helps to promote energy efficiency, occupant comfort and environmental sustainability, aspects of fundamental importance in the current context of growing environmental awareness and the search for more sustainable energy solutions.
Calculation of winter heat requirements
This program calculates the quantity of heat needed to heat the rooms and calculates the number of elements that make up the radiators (aluminium and cast iron).
.
How to calculate the number of elements that make up the radiators and their cost.
How to calculate the potential of the heat generator.
Calculations made in the International System and in the British Imperial System.
Process that allows you to quickly calculate the winter heat requirement expressed in kW - kcal / h - BTU - kJ, needed to heat an environment.
This potential is applicable to any other final heating system (fan coils, radiant panels, floor coils, etc.).
The program also sizes the necessary aluminum or cast iron radiant elements and calculates their cost.
Indicates the required capacity of the heat generator.
Calculation of aluminum radiators

Calculation of cast iron radiators
See also how to calculate the domestic hot water tank:
"Calculation of capacity and thermal power of the domestic hot water tank".
There are detailed instructions and demonstration videos.
Instructions
Let's see in detail how the program works.
The program, after entering the required data, automatically calculates the winter heating requirement, calculates the potential of the heat generator, carries out the sizing and indicates the quantity of the elements that make up the radiators. By entering the cost per element, you also obtain the total amount to build the system (radiators only).
It also calculates how many elements of non-standard heights and returns are needed to obtain the same results.
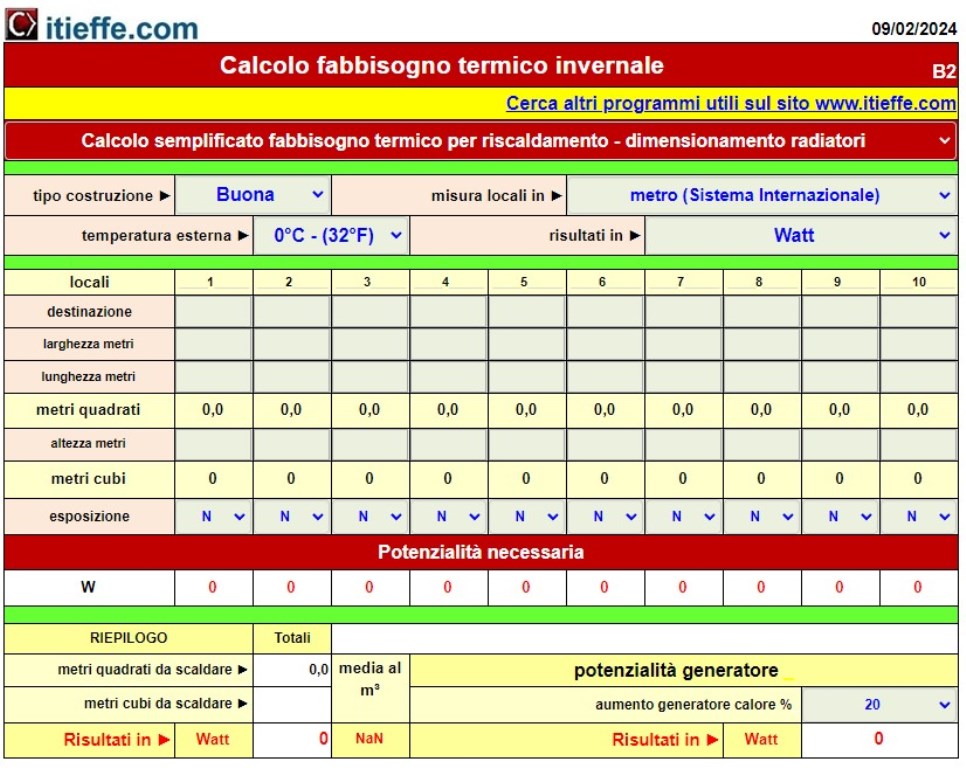
Let's start with data entry

Let's see the detail
1 - type of construction: make a choice in the drop-down menu choosing between "excellent and bad" (you should know how it is built);
2 - make a choice between meter (International System) and foot (British Imperial System);
3 - outside temperature: indicate the Design temperature of your climatic zone by choosing between -15 and + 5 ° C;
4 - results in: select the unit of measurement established for the calculations (BTU - kcal / h - kJoule - Watt - kW);
5 - enter the destination and the linear measurements of the premises,
6 - height: indicate the values;
7 - exhibition: using a map, identify and report it;
8 - insert the safety percentage increase of the heat generator (between 10 and 25%).
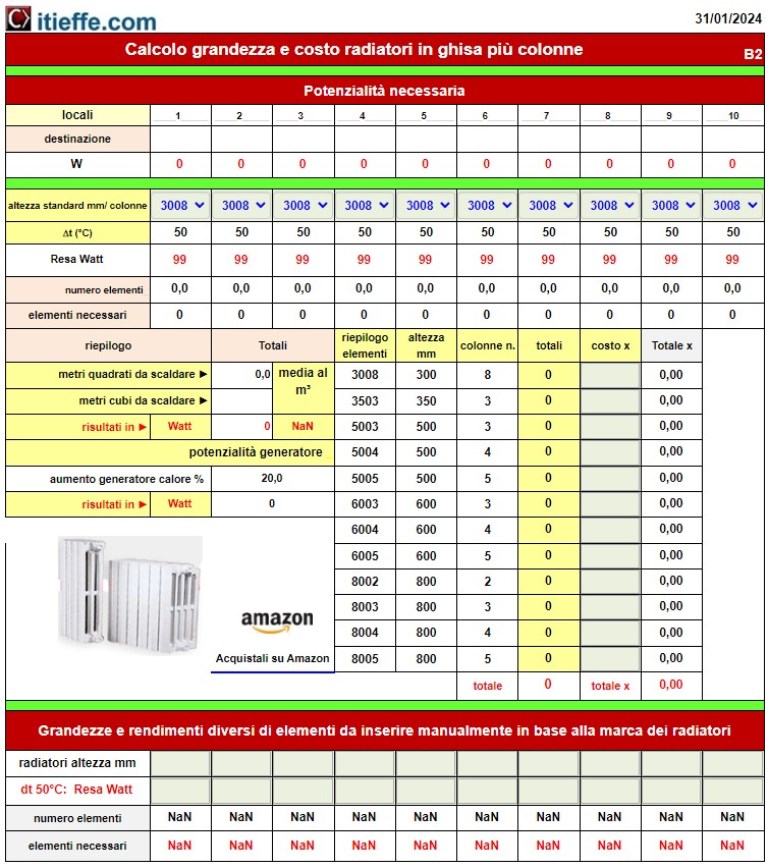
Section for the calculation of aluminum radiators
9 - standard center distance radiators mm: according to the space available to install the radiators, choose an appropriate center distance;
10 - we insert the cost in the desired currency of each single element;
11 - insert radiators with different center distances and yields (heated towel rails).
End of data entry.
Section for the calculation of cast iron radiators
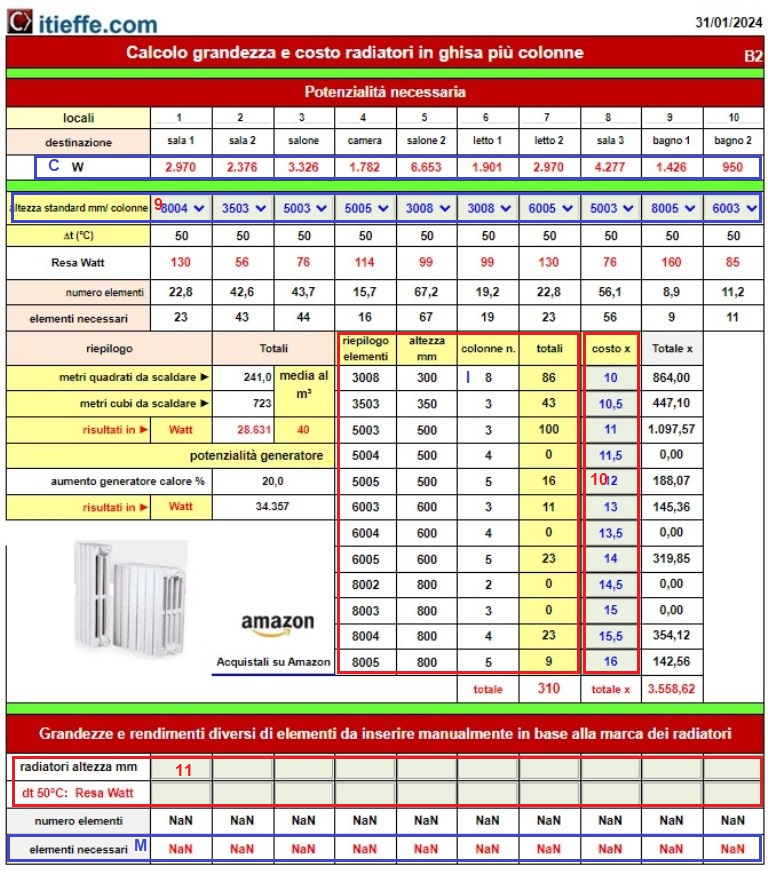
9 - cast iron radiators height in mm by number of columns based on the spaces available to install the radiators, choose an appropriate center distance and number of columns;
10 - we insert the cost in the desired currency of each single element;
11 – insert radiators with different center distances and efficiency (decorative radiator type).
End of data entry.
Once the data entry phase is over, let's analyze the results.
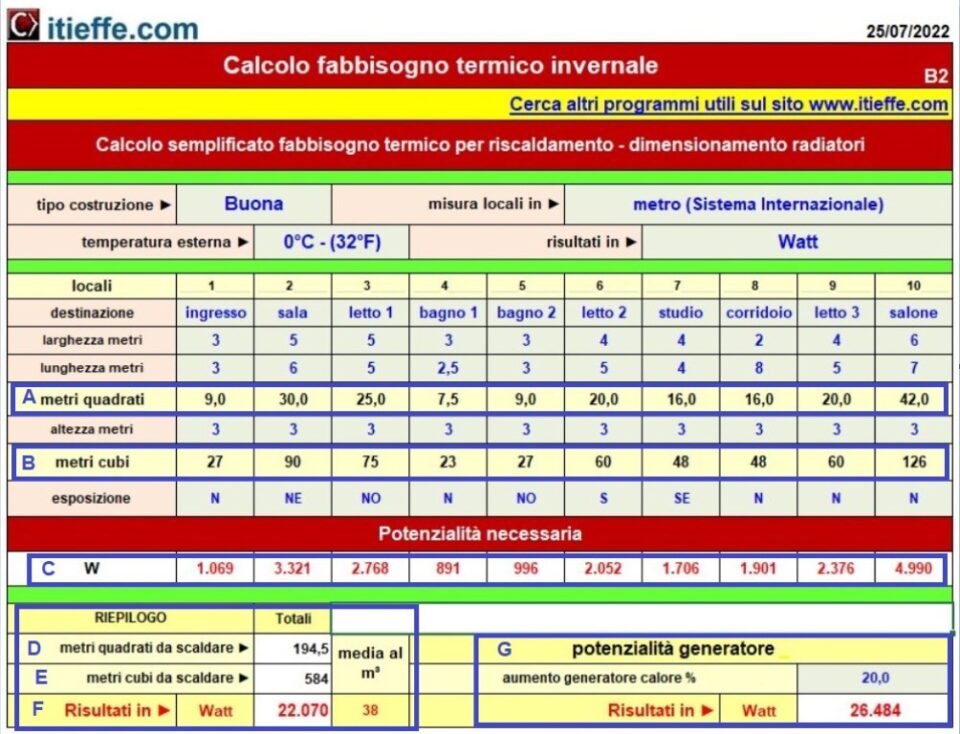
Let's see the detail
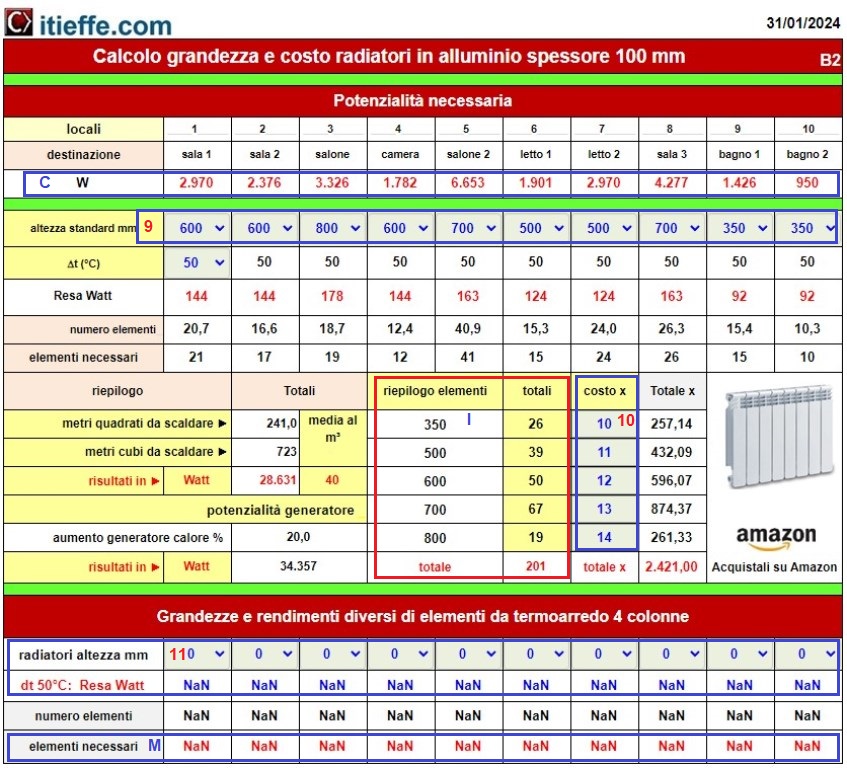
A – meters or square feet to be heated for each individual room;
B – meters or cubic feet to heat for each individual room;
C - energy needed to heat each single room expressed in the measure indicated in point 4 (Results in ►). Energy can also be exchanged with other heating systems (fan coils, radiant panels, floor coils, etc.).
D- total meters or square feet to be heated;
E – total meters or cubic feet to be heated;
F - results in the chosen unit of measurement;
G – generator potential;
I - summary of the size and number of elements needed;
M - real number of elements needed.
There are many types of radiators: heated towel rail, thermo furniture etc. (see offers on Amazon).
In this regard, in the last section of the program, it is also possible to calculate elements of different invoices

Enter the data where requested, you will find the number of elements necessary to provide heat to the rooms involved.
good job
itieffe.com >>> Watch the video ▼
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Heating - Plumbing
- Pipelines
- Heating tables
- pumps
- Heating drawing diagrams
- Domestic hot water
- Combustible gases
Calculation of winter heat requirements
The program below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE
