Refrigerant temperature pressure ratio
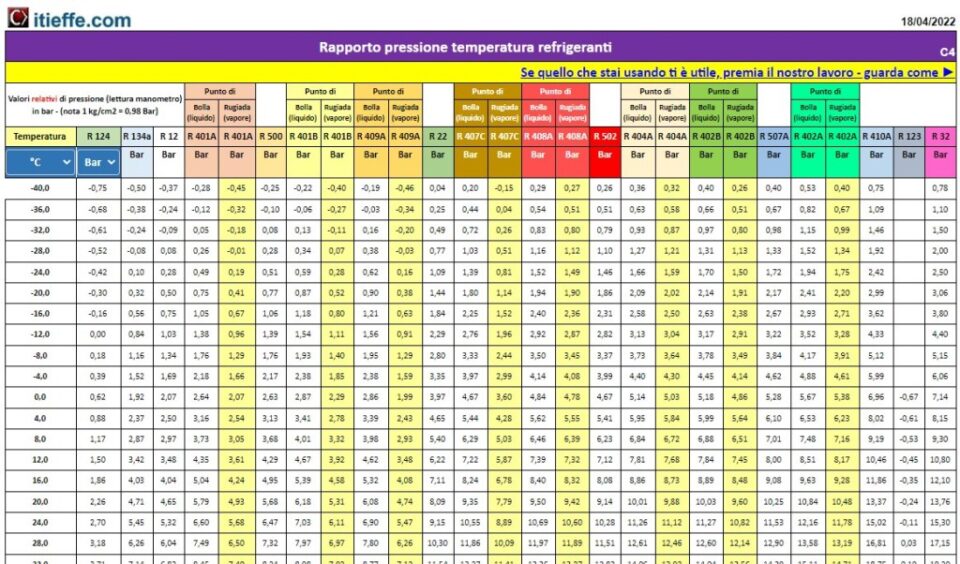
Easy comparison table between the pressure and temperature ratio of the refrigerant gases. The pressure can be indicated in bar and psi, the temperature in degrees centigrade and Fahrenheit.
This document created by Itieffe is a fundamental reference tool for anyone who works in the field of refrigeration, air conditioning and thermal engineering. This document provides essential information on the relationship between the pressure and temperature of refrigerants used in various applications, offering practical guidance for understanding and using this data effectively.
In the field of refrigeration and air conditioning, the relationship between pressure and temperature is crucial for the correct operation and design of the systems. Knowing this relationship allows you to monitor and control the thermodynamic cycle of refrigerants, allowing operators to optimize energy efficiency, desired temperature and equipment life.
With this paper, we will explore in detail how pressure and temperature are related in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Specific data relating to the most common refrigerants will be presented, explaining how to read and interpret pressure-temperature values to determine operating and evaporation and condensation conditions.
It is crucial to highlight that the responsible management of refrigerants is crucial for environmental sustainability, given that many refrigerants are potential greenhouse gases. Therefore, understanding how pressure and temperature influence the behavior of refrigerants is essential for the sustainable design and use of refrigeration and air conditioning systems, contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change.
Refrigerant temperature pressures ratio
Easy comparison table between the pressure and temperature ratio of the refrigerant gases. The pressure can be indicated in bar and psi, the temperature in degrees centigrade and Fahrenheit.
For the zeotropic mixtures the values of both the bubble point and the dew point are indicated.
The zeotropic mixture is characterized by the fact that when the liquid and the vapor are in equilibrium, (saturation), the composition of the liquid differs from that of the vapor, causing different pressure-temperature values for saturated liquid and saturated vapor, which in turn they cause a "glide" of the saturation temperature, both in evaporation and condensation. Practically, the fluid begins its phase of change of state at one temperature and ends it at another, that is, the temperature of the change of state is not constant, as is the pressure and as it happens in "pure" gases (R22, R134a, etc.).
For near azeotrope mixtures (such as R410A, for example) with very low temperature glide, only one temperature is indicated.
azeotropic mixture is a mixture of two or more liquids that do not change their composition by simple distillation (without change during boiling).
The pressure values are subject to rounding
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
Refrigerant temperature pressures ratio
The program / paper shown below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE
