Characteristic values of three-phase refrigeration compressors
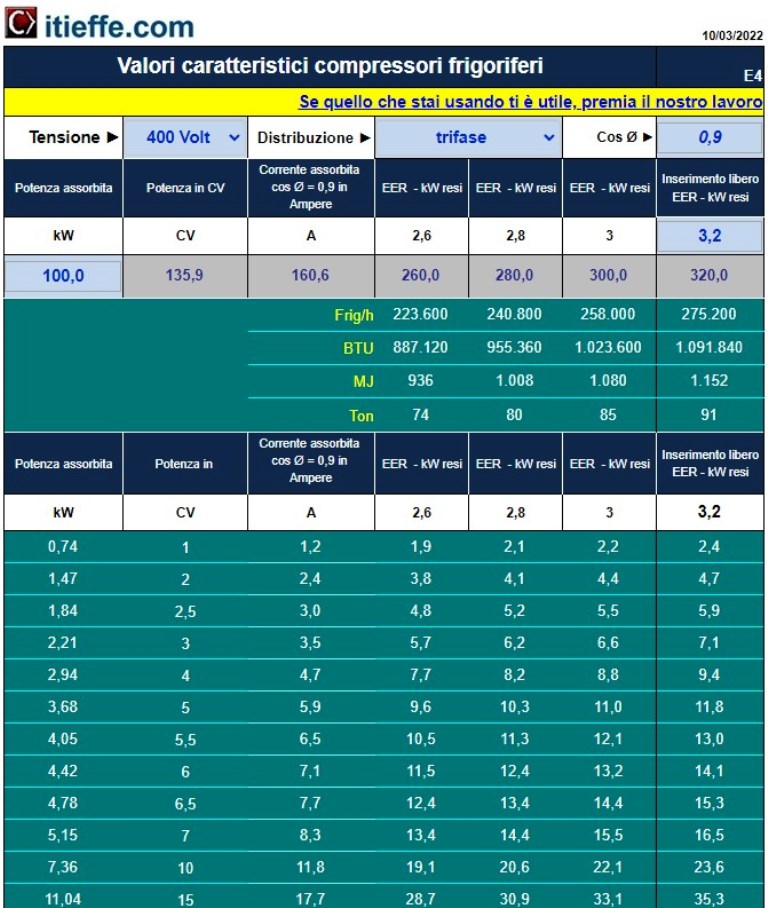
Program that calculates the characteristic values of refrigeration units, compressors, heat pumps, based on the power absorbed. By entering the machine's absorption, it indicates how much it is able to produce in terms of potential at different yield coefficient values. It is possible to enter the yield coefficient directly (EER). Returns results in thermal kW, kcal/h, BTU, MJ and Ton. It also gives the result in Horsepower (CV) and indicates the current required (Amperes) at the various voltages.
Refrigeration compressors are central components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. They play a critical role in the thermodynamic cycle that allows heat to be transferred from one environment to another, maintaining optimal temperatures for the preservation of food, industrial products, and for environmental comfort. To fully understand the operation and efficiency of a refrigerator compressor, it is essential to familiarize yourself with its characteristic values.
This program was created by Itieffe, to offer a clear and complete explanation of these fundamental values and to illustrate how they influence the overall performance of refrigeration compressors. This tool is designed to be an educational and practical resource for engineers, technicians, designers, and professionals in the HVAC-R (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration) industry, as well as anyone involved in the selection, installation, or maintenance of refrigeration systems.
Within the program, you will find detailed explanations on the main characteristic values of refrigeration compressors, including the efficiency coefficient (EER), the power and the current absorbed by the compressor.
Understanding these values is critical to selecting, designing and maintaining efficient and economical refrigeration systems. We trust that this program will become a valuable tool to gain in-depth knowledge on this technical topic and contribute to improving the energy and environmental performance of refrigeration systems.
Characteristic values of refrigeration compressors
Characteristic values of refrigeration compressors
Elaborate that calculates the characteristic values of refrigeration units, compressors, heat pumps, based on the absorbed power.
By inserting the absorption of the machine, it indicates how much it can produce in terms of potential at the different yield coefficient values.
It is possible to enter the yield coefficient directly (EER).
Returns results in thermal kW, kcal/h, BTU, MJ and Ton.
It also gives the result in Horses (CV) and indicates the current needed (Ampere) at the various voltages.
Indications
| EER | Energy Efficiency Ratio = energy transformation efficiency ratio: W rendered / W absorbed (could also be: frig / h / W absorbed) |
| COP | Coefficient of performance or: useful effect - dimensionless pure number |
| The COP takes on a different connotation depending on whether the refrigeration cycle is responsible for producing cold or producing heat (heat pump). COP and EER do not constitute efficiency and are therefore always greater than 1. They only define the degree of heat transfer for each unit of energy supplied from the outside. | |
| COP |
for the production of cold: |
| It can be determined on the pressure-enthalpy diagram by making the ratio between the cooling effect and the thermal equivalent of the compression work: | |
| COP = cooling effect / heat of compression | |
| COP |
for the heat pump cycle: |
| In this case the required effect is heating. Therefore the sum of the cooling effect and the thermal equivalent of the compression work, which constitutes the available heat, must be considered. It must be divided by the thermal equivalent of the compression work: | |
| COP = (cooling effect + compression heat) / compression heat | |
| It should be noted that some texts report the COP as the ratio between: Power output / power absorbed in the same way as the EER | |



Instructions
How to proceed
1 - choose the voltage of use among the preset values.
2 - choose how the distribution will take place between single and three phase.
3 - indicate the value of the phase shift Cos Ø.
4 - insert the EER value that can be found (see indications present in the paper).
5 - enter the value of the power absorbed by the compressor in kW
6 - we can view the present results. The values in Horsepower (CV) and in Ampere (A) of the machine are indicated, as well as the kW obtained on the basis of different compressor efficiency (EER).
7 - summary of the power output values according to different units of measurement.
8 - table with fixed values for easy visual use.
Let's take an example.
We have a compressor that absorbs 100 kW which is powered by a single-phase 400 V voltage.
The phase shift (Cos Ø) is equal to 0,9.
Calculate the absorbed current.
Let's put the data into the program and see what it indicates.
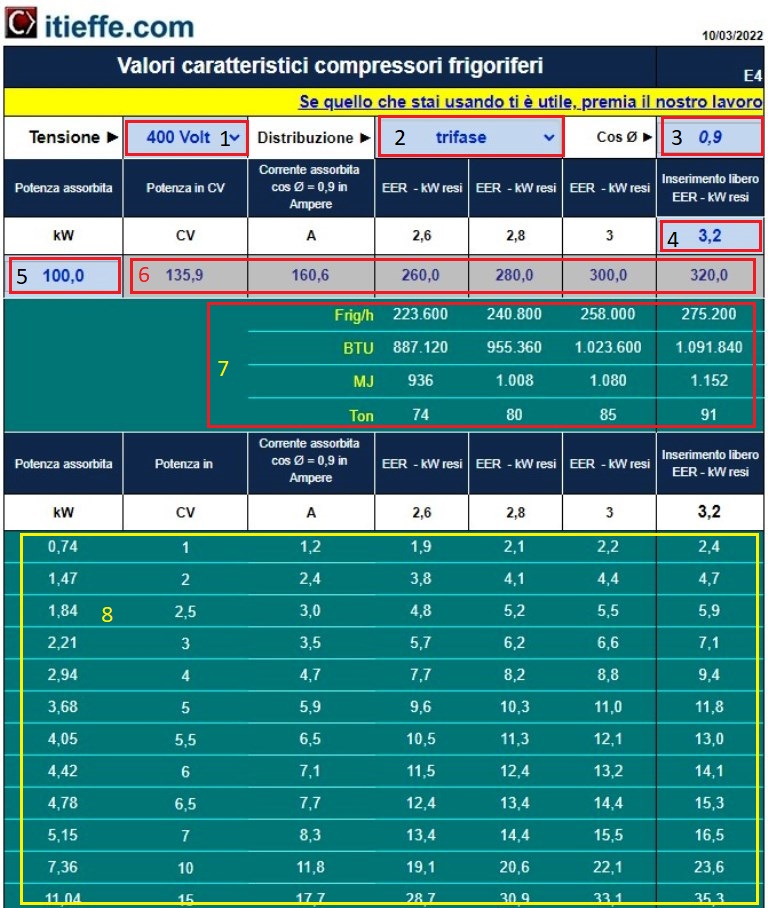
The current is equal to 160,6 Ampere.
Now based on the efficiency of the refrigeration compressor, through the EER ratio (Energy Efficiency Ratio = energy transformation efficiency ratio: W rendered / W absorbed) which we assume is 3,2, indicatively we have the thermal power that the machine can supply that is, in this case, 320 thermal kW).
Section 7 shows the results of the thermal power obtained in Frig / h - BTU - MJ - Ton (Frig / h i.e. frigories / hour, equivalent to kcal / h i.e. kilocalories / hour) in the various cases of EER.
Easier than that
good job
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Air conditioning
- Air ducts
- Ventilation systems
- Autonomous air conditioners
- Psychrometric charts
- Air conditioning tables
- Air quality
- Conditioning diagrams & drawings
Characteristic values of three-phase refrigeration compressors
The program below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE
