General electrical cables indications

Italian national cables, harmonized cables, main CEI standards, identification of cable cores, types of installation
Electrical cables form an essential part of electrical infrastructure around the world. They are used for the safe and efficient transport of electricity in various sectors, from industrial applications to energy distribution networks and domestic systems. The correct selection, installation and management of electrical cables are essential to ensure the safety, reliability and efficiency of electrical systems.
The reason for this guide
This guide was created by Itieffe to offer a comprehensive overview of this crucial topic; provides clear and detailed information on a number of aspects relating to electrical cables, including:
- Italian national cables: information is provided on the specifications of electrical cables produced in Italy, including their standards and reference regulations.
- Harmonized cables: This section covers electrical cables that meet European harmonized standards, ensuring compliance with safety and performance requirements.
- Main CEI Standards: the role of the Italian Electrotechnical Committee (CEI) standards in the regulation of electrical cables and in the promotion of best practices is examined.
- Identification of cable cores: This part explains how to identify and understand the different cores within electrical cables, including conductors, insulation and shielding.
- Main Laws: The legal and regulatory frameworks that regulate the use of electrical cables are examined, ensuring safety and compliance.
- Types of laying: This section provides an overview of the different ways of installing electrical cables, such as installing underground, overhead or in ducts.
Conclusions
Understanding these aspects is essential to ensure that electrical cables are used safely and compliantly with regulations, avoiding safety problems and efficiency losses. This guide aims to be a valuable resource for engineers, technicians, designers, installers and anyone involved in managing electrical systems and choosing the most suitable cables for their specific applications.
General electrical cables indications
Italian national cables, harmonized cables, main CEI standards, cable core identification, main laws, types of laying
General electrical cables indications
Index of topics
| 1 | Italian national cables |
| 2 | Harmonized cables |
| 3 | Main CEI standards |
| 4 | Identification of cable cores |
| 5 | Types of laying |
1) Italian national cables
Identification system of Italian national cables according to CEI UNEL 35011
Degree of flexibility of the conductor
| A | Aluminum conductor |
| F | Flexible rope |
| FF | Extremely flexible rope |
| R | Rigid rope |
| S | Sectoral chord |
| U | Single thread |
Nature and quality of the insulation
| E | Thermoplastic polyethylene based insulation |
| E4 | Cross-linked polyethylene at a characteristic temperature of 85 ° C |
| G | Insulation based on natural and / or synthetic rubber |
| G7 | Insulator based on ethylene propylene rubber at a characteristic temperature of 90 ° C |
| G9 | Insulation based on cross-linked elastomer with low emission of fumes and toxic and corrosive gases at a characteristic temperature of 90 ° C |
| G10 | Insulation based on cross-linked elastomer with low emission of fumes and toxic and corrosive gases at a characteristic temperature of 90 ° C |
| R | Insulation based on polyvinyl chloride at a characteristic temperature of 70 ° C, quality TI1-TI2 |
| R2 | Insulation based on polyvinyl chloride at a characteristic temperature of 70 ° C, quality R2 |
| R7 | Insulating compound based on polyvinyl chloride at a characteristic temperature of 90 ° C, quality TI3 |
Screens
| H | Metallized paper or aluminum tape screen |
| H1 | Screen with strips or strips or copper wires |
| H2 | Copper braid or braid screen |
Armature
| A | Braid or metal braid armor |
| F | Armor with cylindrical wires, usually of steel |
| N | Ribbon armor, usually made of steel |
| Z | Steel plate armor |
Nature of the sheath
| E | Thermoplastic sheath |
| E4 | Cross-linked polyethylene |
| G | Natural and / or synthetic rubber sheath |
| K | Sheath based on polychloropropylene |
| R | Polyvinyl chloride based sheath |
| M1 | Sheath made from thermoplastic material with low emission of toxic and corrosive fumes and gases |
| M2 | Elastomeric sheath with low development of toxic and corrosive fumes and gases |
Form of cables
| O | Cylindrical shaped cable |
| D | Flattened shape cable |
| X | Cores assembled in a visible helix (eg cord) |
| W | Flat divisible cable |
Possible supporting organ
| S | Main body generally metallic incorporated in the sheath |
| Y | Textile or metal bearing organ, included between the cores or tied externally to the cable |
General electrical cables indications
Example of an identification:
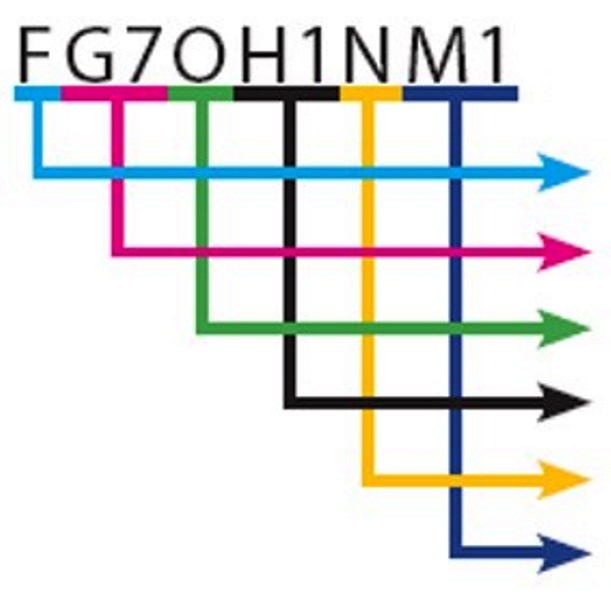
| Example | |
| ► | Flexible conductor |
| ► | G7 quality insulation |
| ► | Cylindrical |
| ► | Copper strip screen |
| ► | Steel strip armor |
| ► | Sheath of M1 quality |
General electrical cables indications
2) Harmonized cables
Harmonized cable designation system according to CENELEC HD 361 (CEI 20-27)
Reference of standards
| H | Cable compliant with harmonized standards |
| A | Nationally recognized cable |
| N | National type cable |
Nominal tension
Uo / U: where Uo is the rms value between any of the conductors and earth and U is the rms value of the voltage between any two conductors of the cable
| 00 | Less than 100/100 V |
| 01 | Higher than 100/100 V and lower than 300/300 V |
| 05 | 300 / V 500 |
| 07 | 450 / V 750 |
| 1 | 0,6 / 1 kV |
Insulation and sheath material
| B | Ethylene propylene rubber at a characteristic temperature of 60 ° C |
| N | Polychloroprene |
| N2 | Polychloroprene for welding cables |
| Q | polyurethane |
| R | Rubber |
| V | Commonly used PVC |
| V2 | PVC for operating temperatures of 90 ° C |
| V3 | PVC for cables installed at low temperatures |
| V4 | Cross-linked PVC |
| V5 | Oil resistant PVC |
| Z | Compound based on polyolefins |
Screens
| C | Concentric copper conductor |
| C4 | Copper braid screen on all cores |
| C5 | Copper braid screen on the single cores |
| C7 | Copper screen consisting of wires or strips or strips |
Armature
| Z2 | Round steel wire armor |
| Z3 | Steel plate armor |
| Z4 | Steel strip armor |
| Z5 | Steel wire braid |
Construction form of the cable
| H | Flat divisible cables, with or without sheath |
| H2 | Non-divisible flat cables |
| H3 | Flat cables with cores spaced from a strip |
| H6 | Flat cable with 3 or more cores, according to HD 359 |
| H7 | Cable with double layer insulation applied by extrusion |
| H8 | Extensible cord |
Degree of flexibility of the conductor
| D | Flexible conductor of cables for welding machines |
| E | Extremely flexible conductor for welding cables |
| F | Flexible conductor for cables for mobile installations (class 5 IEC 228) |
| H | Highly flexible conductor for cables for mobile installations (class 6 IEC 228) |
| K | Flexible cable conductor for fixed installations (class 5 IEC 228) |
| R | Rigid, round, stringed conductor |
| U | Rigid, round, single-wire conductor |
Example of an identification:
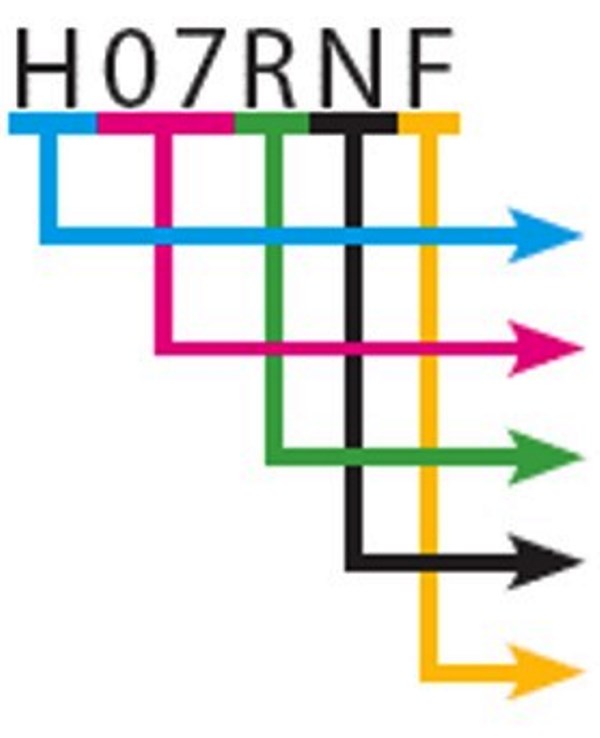
| Example | |
| ► | Harmonized type cable |
| ► | Rated voltage 450/750 V |
| ► | Ethylene propylene rubber insulation |
| ► | Polychloroprene sheath |
| ► | Flexible conductor |
3) Main CEI standards
List of the main CEI standards relating to cables
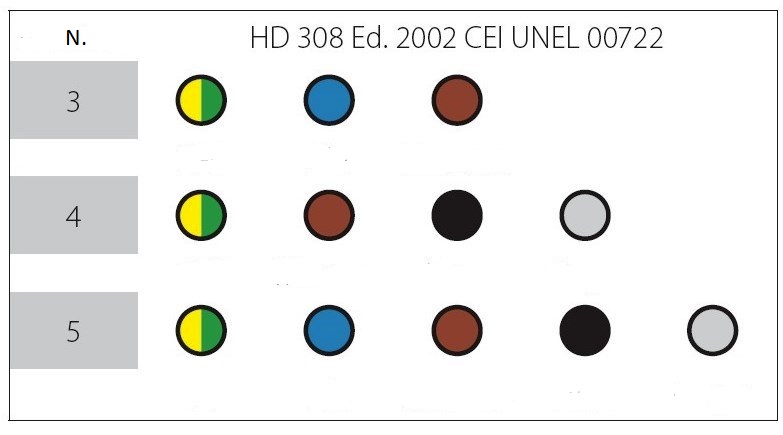
| CEI-UNEL 00722 table | HD 308 | Distinctive colors of insulated cable cores |
| CEI-UNEL 35011 table | - | Cables for energy and signaling: designation abbreviations |
| CEI EN 50363 CEI 20-11 | EN 50363 | Technical characteristics and test requirements of compounds for insulation and sheaths of energy cables |
| IEC 20-13 | IEC 60502 | Rubber insulated cables with rated voltage from 1 to 30 kV |
| IEC 20-14 | IEC 60502 | PVC insulated cables for nominal voltages from 1 to 30 kV |
| IEC 20-19 | HD 22 | Rubber insulated cables with rated voltage not exceeding 450/750 V |
| IEC 20-20 | HD 21 | PVC insulated cables with rated voltage not exceeding 450/750 V |
| IEC 20-21 | IEC 60287 | Calculation of the current carrying capacity |
| CEI EN 50266 CEI 20-22 | IEC 60332-3 | Test of fire retardant cables |
| IEC 20-27 | HD 361 | Cable designation system for energy and signaling |
| CEI EN 60228 CEI 20-29 | IEC 60228 / HD 383 | Conductors for insulated cables |
| CEI EN 60811 CEI 20-34 | EN 60811 / HD 505 | Test methods |
| CEI EN 60332 / 1-2 - CEI 20-35 / 1-2 | EN 60332-1-2 / IEC 60332-1-2 | Tests on electrical cables in fire conditions |
| CEI EN 50200 CEI 20-36 | IEC 60331 | Fire resistance test of electric cables |
| CEI EN 50267 CEI 20-37 | EN 50267-2-1 / IEC 60754-1 | Tests on the gases emitted during the combustion of electric cables |
| IEC 20-38 | - | Fire retardant rubber insulated cables with low emission of toxic and corrosive fumes and gases |
| IEC 20-40 | HD 516 | Guide to the use of low voltage cables |
| CEI EN 50414 CEI 20-85 | EN 50414 | Test methods for the analysis of the amount of lead in compounds for insulators, coatings and sheaths |
| - | BS 6004 | PVC insulated cables for electrical power and lighting |
| - | VDE 0250 | Isolierte starkstromleitungen |
| - | DIN 57250 | Isolierte starkstromleitungen PVC mantelleitung mit Tragseil |
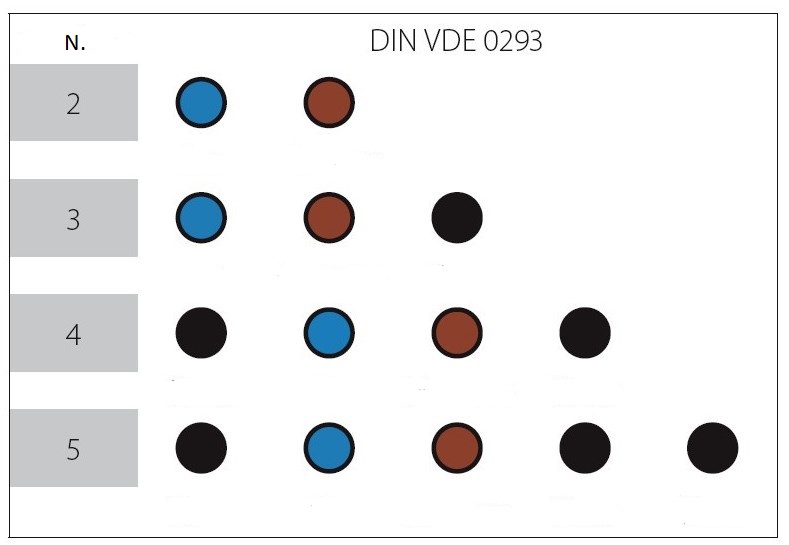
| - | DIN VDE 0293 | Aderkennzeichnung von Starkstromkabeln und-isolierten Starkstromleitungen mit Nennspannung bis 1000 V |
4) Identification of the cores of the cables
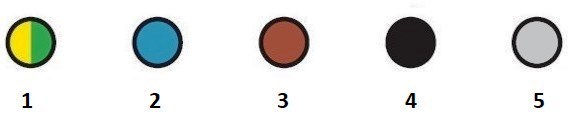
Description
| N. | Number of cables |
| 1 | Yellow green |
| 2 | Blue |
| 3 | Brown |
| 4 | Black |
| 5 | Grey |
Cables with yellow-green protective conductor
Cables without yellow-green protective conductor
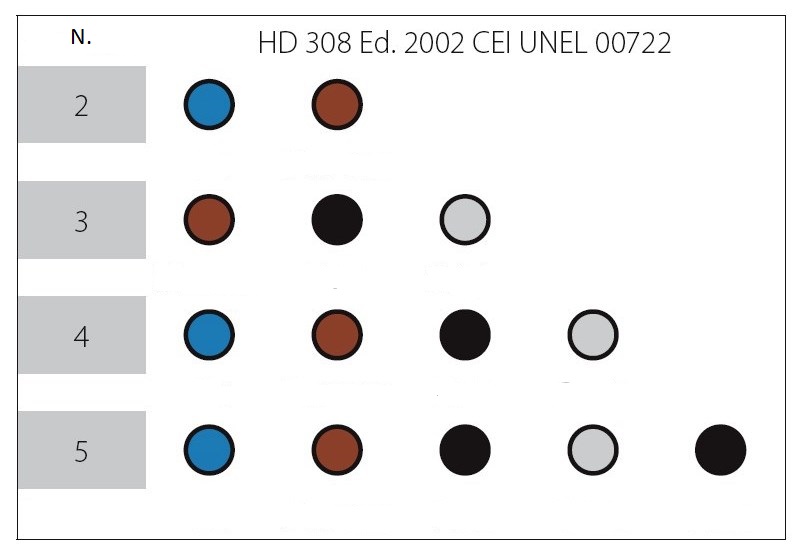
Flexible cables with yellow-green protective conductor
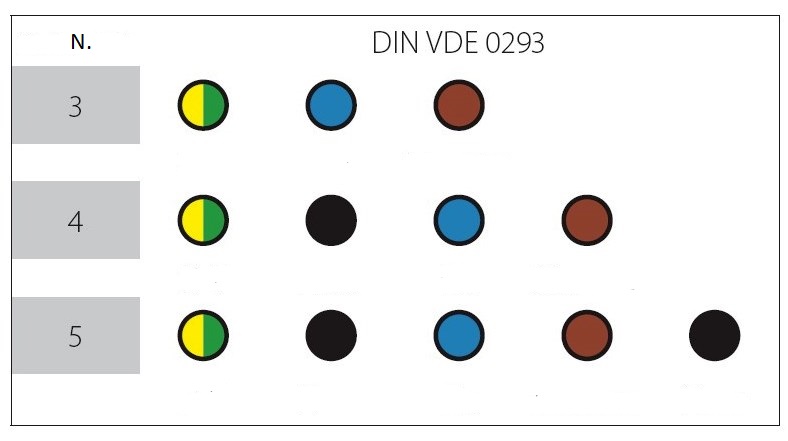
Flexible cables without yellow-green protective conductor
5) Type of installation
Illustrations of some types of cable routing

Sheathless cables in protective tubes embedded in the masonry
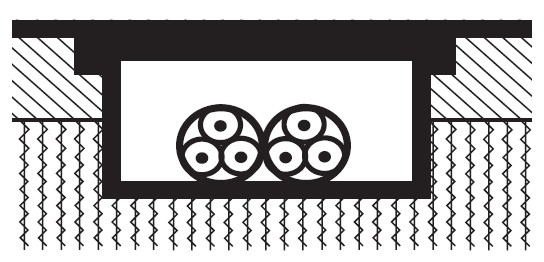
Multi-core cables laid in channels embedded in the floor
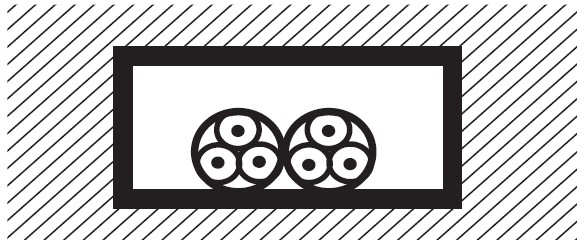
Multi-core cables (or single-core with sheath) in non-circular protective tubes embedded in the masonry
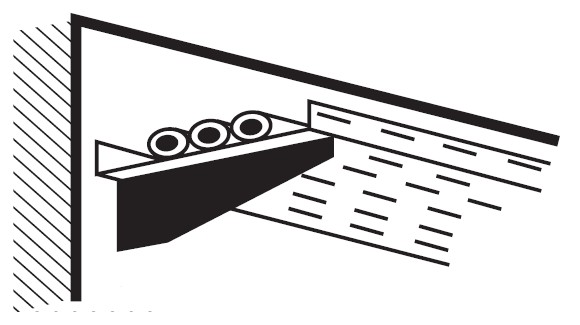
On perforated walkways
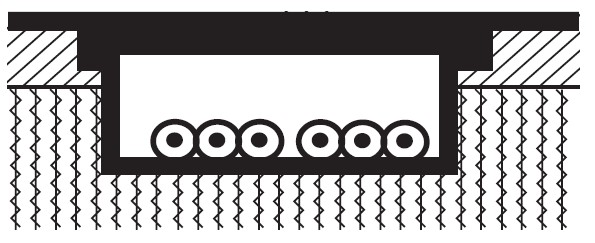
Sheathless cables laid in channels embedded in the floor
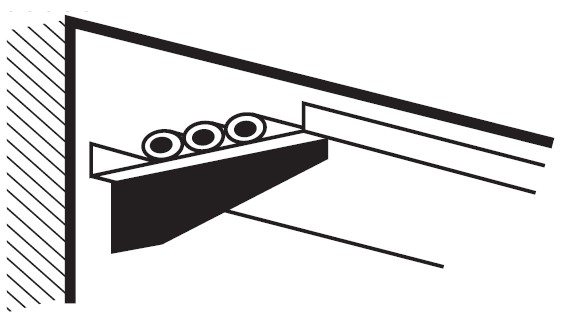
On non-perforated walkways
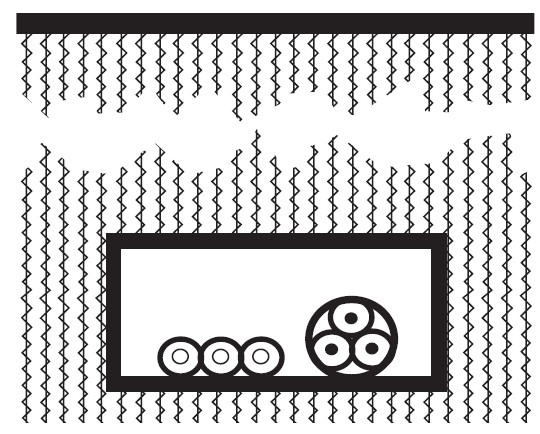
Single-core and multi-core cables in underground protective pipes or in underground tunnels
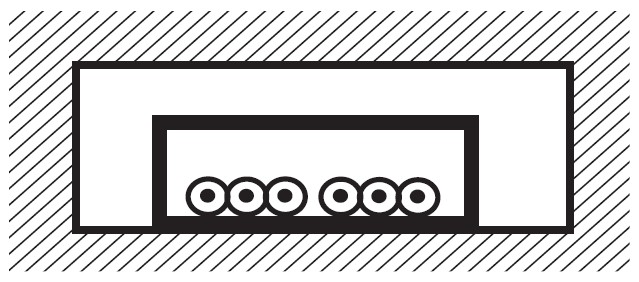
Single-core cables without sheath in non-circular protective tubes laid in structure cavities

Multi-core cables (or single-core with sheath) buried without additional mechanical protection
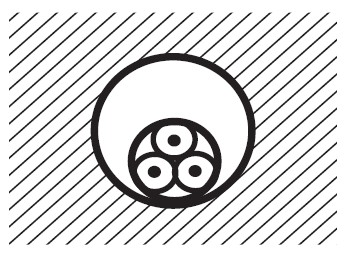
Multi-core cables in protective tubes embedded in the masonry
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Electricity - Electronics
- Calculation of color coded electric resistances
- Electric - electronic tables
- Electrical drawing diagrams
