Calculation of power required for domestic hot water
Calculation of the power required to produce domestic hot water
This program, developed by Itieffe, is an important resource for anyone involved in the design and optimization of domestic hot water (DHW) production systems. This tool stands out for its ability to simplify the calculation of the power required to heat water for domestic use, thus helping to ensure optimal energy efficiency and a reliable supply of hot water.
Domestic hot water is an essential element in every building, from residential homes to commercial and industrial buildings. Designing an efficient DHW system not only improves user comfort, but also helps reduce energy costs and promote responsible use of resources.
This program offers a practical and reliable solution based on specific application needs. With an easy-to-use interface and clear methodology, it allows engineers, designers, installers and industry professionals to obtain precise and useful values for sizing and selecting DHW system components.
One of the strengths of this program is its flexibility, as it allows you to enter different variables such as the inlet water temperature, the desired temperature and other specific information. In this way, it is possible to adapt the calculation to the specific conditions of each project, guaranteeing a customized and optimized design.
Energy efficiency is a crucial goal in the current environmental landscape, and tools like this program contribute significantly to achieving this goal. A correct sizing of the required power not only reduces energy consumption, but also favors the adoption of sustainable solutions in the water-sanitary sector.
We are confident that this program will prove to be an invaluable resource for those wishing to design energy efficient and responsible ACS systems.
Calculation of power required for domestic hot water
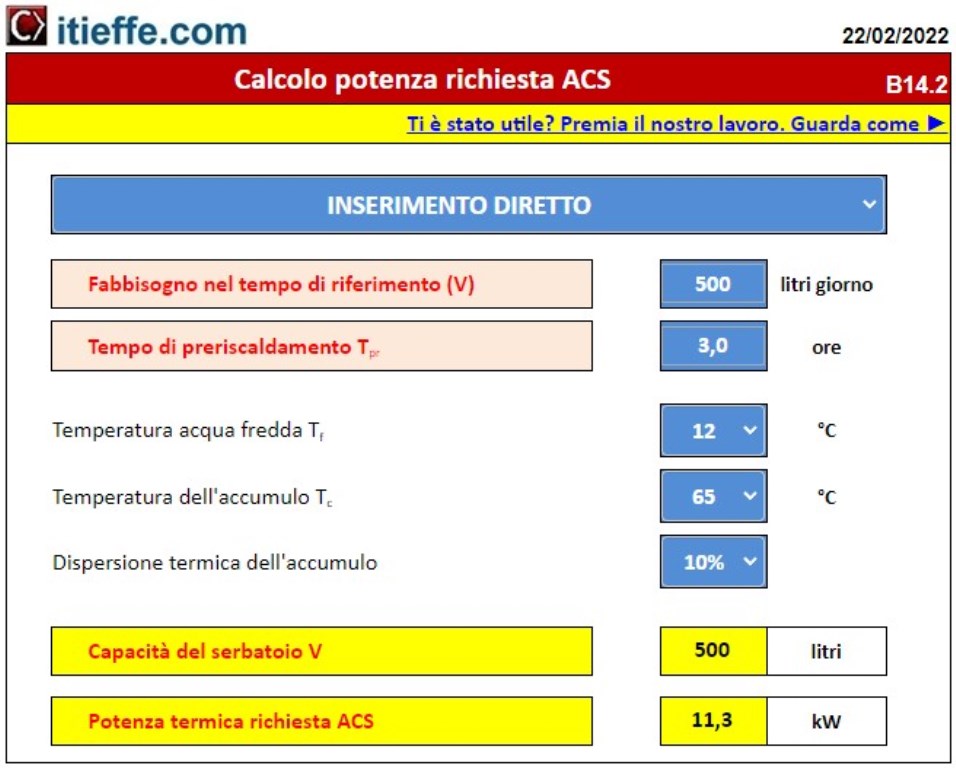
How the power required to produce domestic hot water is calculated.
The calculation is carried out with direct data entry
Calculation of power required for domestic hot water
Let's take an example
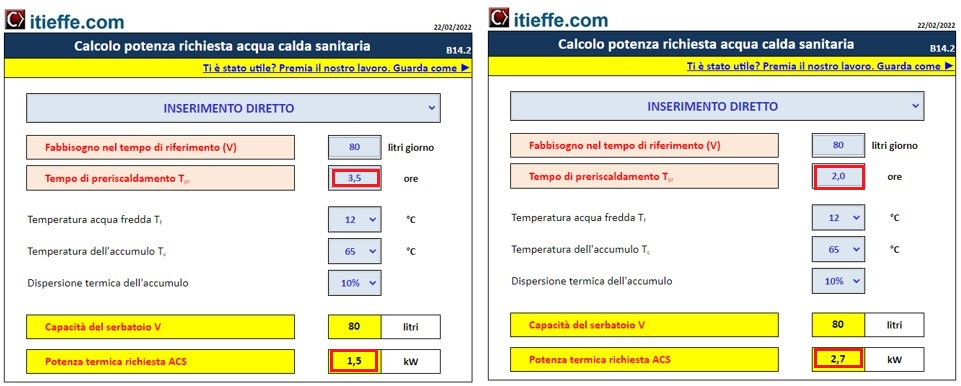
We have a simple 80 liter water heater:
the inlet water temperature is 12 ° C;
the average water temperature inside the water heater must be 65 ° C;
its thermal dispersion is equal to 10% of the heat produced.
Taking into consideration a preheating time equal to 3.5 hours, the thermal power required (electrical resistance or hot water coil) will be equal to 1.5 kW (test carried out with the real data of a water heater with commercial electrical resistance).
For a shorter preheating time, the required heat output will increase proportionally.
For example, if the preheating time is to be reduced to 2 hours, the required thermal power must be equal to 2.7 kW.
Longer preheating times, while considerably lowering the required thermal power, could make the system uneconomical due to the predominance of the thermal dispersion involved.
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Heating - Plumbing
- Pipelines
- Heating tables
- pumps
- Heating drawing diagrams
- Domestic hot water
- Combustible gases
The program below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE

