Simple general indications that can be of help for those who want to see how to proceed in designing a heating system from A to Z
Designing an effective and efficient heating system is a process that requires a strategic approach, technical knowledge and a thorough understanding of the needs of the environment and users. In a context where energy efficiency and resource optimization have become fundamental priorities, the design of a heating system requires a careful balance between thermal comfort, energy consumption and environmental impact.
This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key steps involved in the heating system design process, offering guidelines and practical advice to address common challenges and achieve high quality results. From assessing the thermal needs of the building to selecting equipment, from designing the system to commissioning it, we will explore each stage with attention to detail and the search for innovative solutions.
It will be essential to understand the various technologies available, from traditional boiler systems to radiant heating solutions and heat pump systems, considering the advantages and disadvantages of each option based on the specific context.
Collaboration with industry professionals, such as thermotechnical engineers and plant designers, is essential to ensure that the project is aligned with current safety standards and regulations. However, a good understanding of the basics of heating system design will enable the project managers involved to actively participate in the decision-making process and contribute significantly to the final solutions.
HOW TO DESIGN A HEATING SYSTEM
We remind you that the main objective in designing a heating system is to achieve a balance between the comfort of the occupants, energy efficiency and environmental sustainability. Through this guide, we will explore the strategies and methodologies that allow you to achieve this goal, facilitating the creation of welcoming, efficient and environmentally friendly interior environments.
Before we dive into the details, It is important to underline that the design of a heating system requires a multidisciplinary approach and a constant attention to innovation and best practice in the sector. In this spirit, we invite readers to explore the various aspects of heating system design and to face this challenge with enthusiasm and determination, to create comfortable and sustainable environments for present and future generations.
HOW TO DESIGN A HEATING SYSTEM
Simple general indications that can be of help for those who intend to see how to proceed in the design of a heating system from A to Z.
The heating system (see current legislation) is carried out on the basis of a project drawn up by a heat engineer (unless powers below 15 kW), takes into account the characteristics of the site, the exposure, the climatic zone and the personal needs of each.
Domestic heating systems are divided into two main types:
- centralized
- autonomous
In this exhibition, autonomous systems will be treated in particular.
A heating system is a complex of elements and equipment designed to maintain temperature values higher than the external ones in certain environments.
Main components of a typical scheme for domestic use:
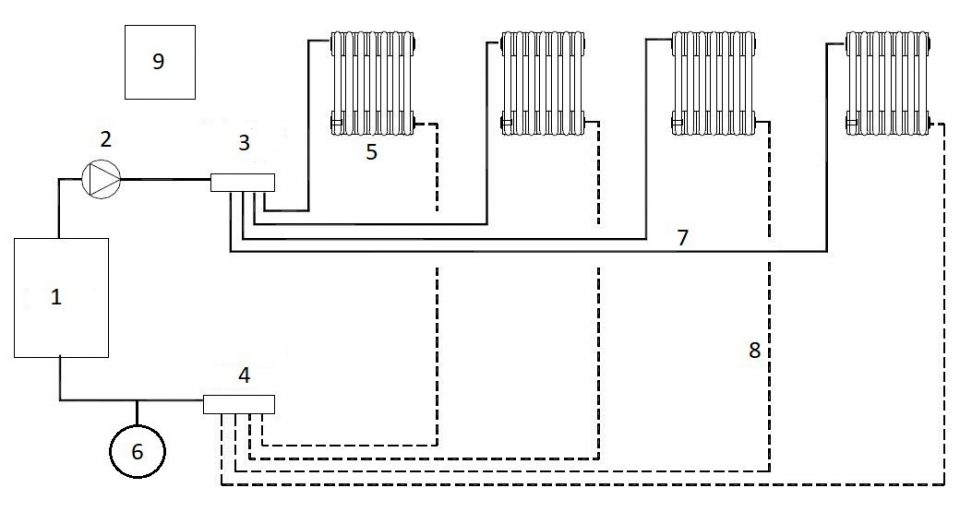
- heat generator;
- circulation pump;
- hot water delivery distribution manifold;
- hot water return distribution manifold;
- terminal elements;
- expansion tank;
- hot water delivery pipes;
- hot water return pipes;
- electric power and control panel.
Heat generators
Heat generators differ from each other by the energy source with which they are powered
Main energy sources:
- Methane is the one most used by most Italian households, due to its widespread distribution and limited expenditure compared to other fuels.
- Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) is mainly used where methane does not reach. It is not cheap at all.
- Diesel fuel is still used in some special cases and it too is not cheap.
- Pellets and wood, more and more people are turning to this energy source which offers considerable savings in operation even if their use involves additional work on the part of the user (but do you want to say how fascinating it is to watch the flame burn?) .
- Heat pumps (intended as an air conditioner operating in reverse cycle), increasingly used and with operating costs among the lowest among the distributed energies.
In this discussion, the use of heat pumps is not explored as, for the same environment, the design is made in the summer regime which remains valid also for the winter one. Please refer to the section: "How to design air conditioning system".
Note: it should be considered that heat pump heating sets limits: the lower the external temperatures, the corresponding decrease in the proportional yield (the colder it is, the less the heat pump yields).
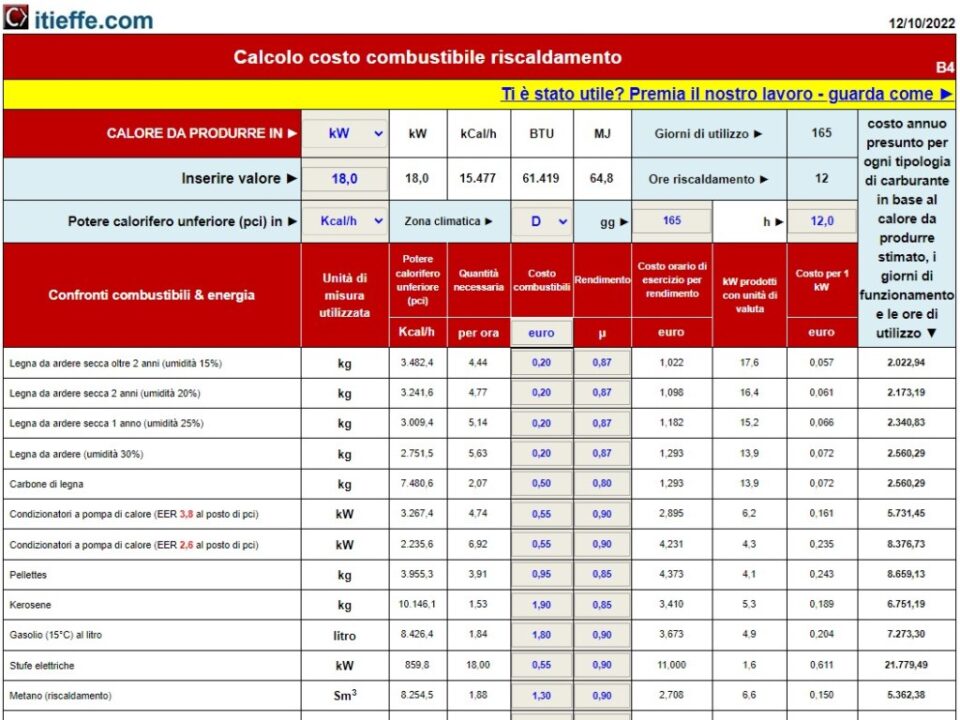
The following program analyzes the operating cost for each single type of energy used in relation to the potential necessary for the environment:
Note: it is advisable to calculate the capacity of the heat generator before using the program.
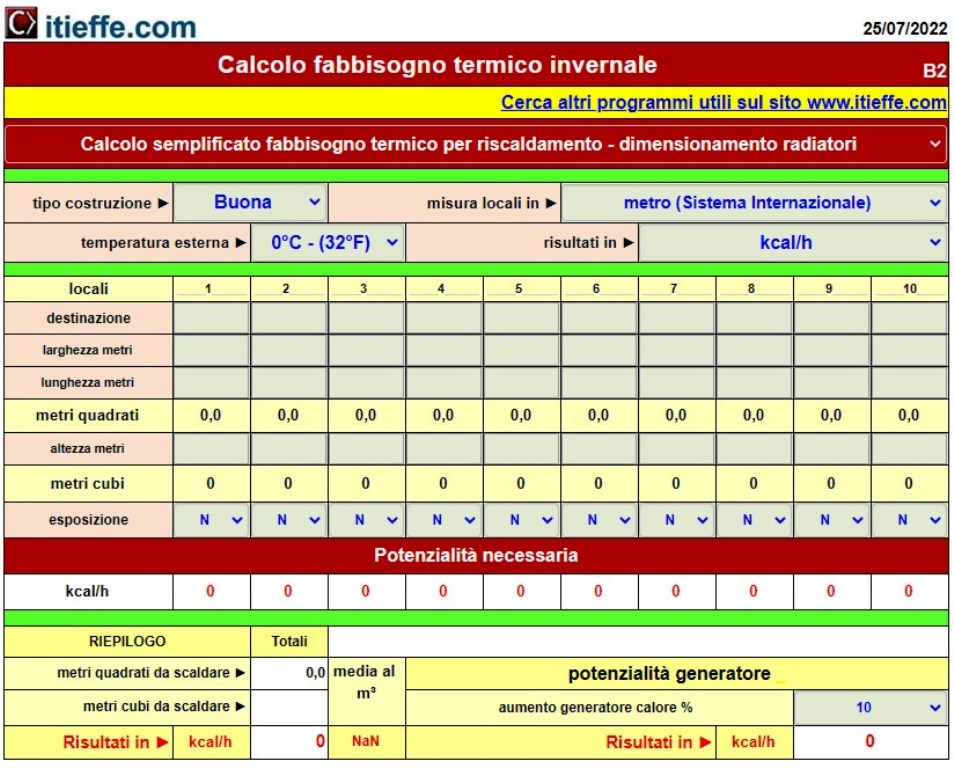
To calculate the capacity of the heat generator to be installed in an environment, refer to the following program:
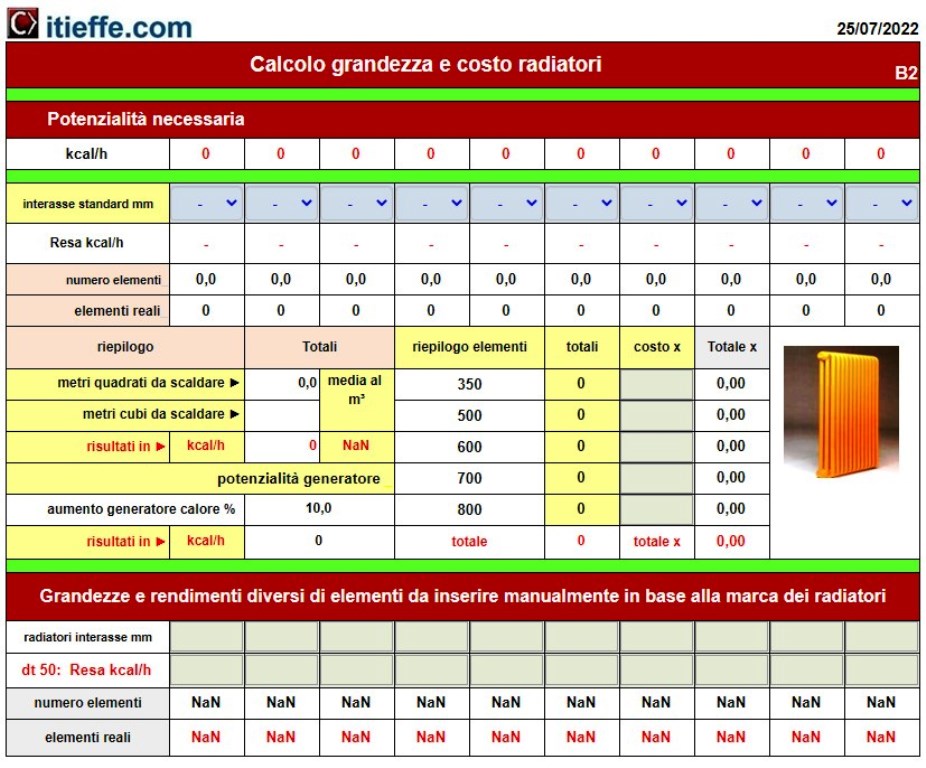
With the same program, it is also possible to calculate the radiators and determine their price
The final line indicates the value in Watts that the heat generator must supply to the system (26.484 W = 26,5 kW).
The circulation electropumps
They are necessary for the circulation of fluids within the hydraulic circuit.
Natural circulation systems (radiators) in which the movement of water is caused by temperature differences, have not been used for years.
Nowadays, only forced circulation systems are used, which is carried out by means of electric fluid circulation pumps.
Circulation pumps perform the function of overcoming localized and distributed pressure drops. What we will consider, are exclusively centrifugal pumps.
A pump is characterized by two parameters: flow rate and head which determine its choice.
The flow rate is determined by the thermal (energy) needs of the site and by the thermal difference between the inlet and outlet temperatures of the water.
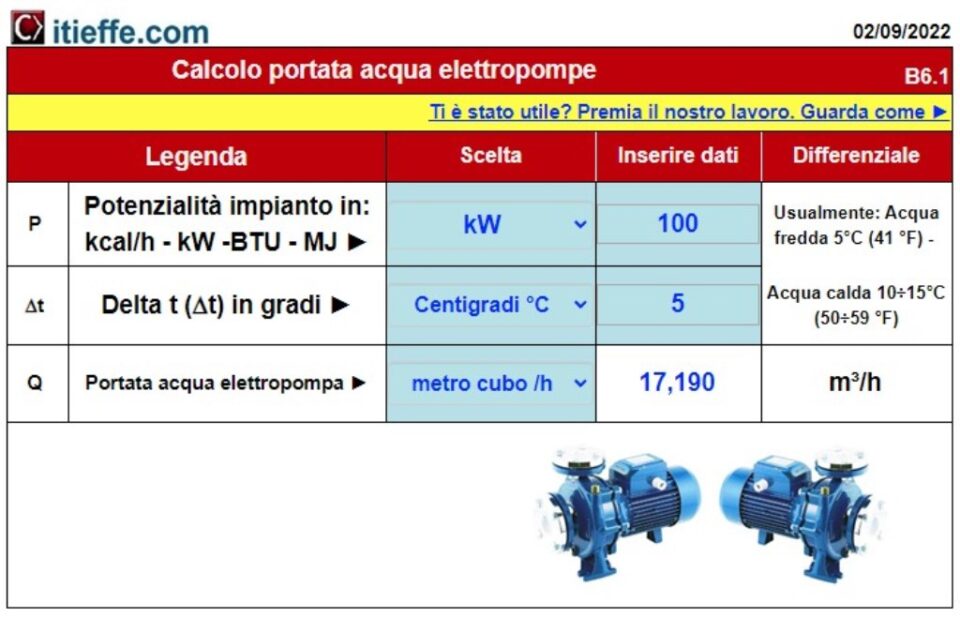
While the circulators (small electric circulation pumps) are already inserted in almost all boilers for domestic use, if it is necessary to make a precise calculation of the electric pumps, the following program can be used:
From here we get the cubic meters per hour that must circulate (in this case 2,3 mc / h) in the circuit to supply the necessary (thermal) kW and with the required delta t (∆t 10).
By adding the head calculation it is possible to determine the power of the pump to be installed.
To calculate the head required for the circuit, it can be traced back to it by calculating the head losses achieved with the following programs (also valid for the sizing of the pipes):
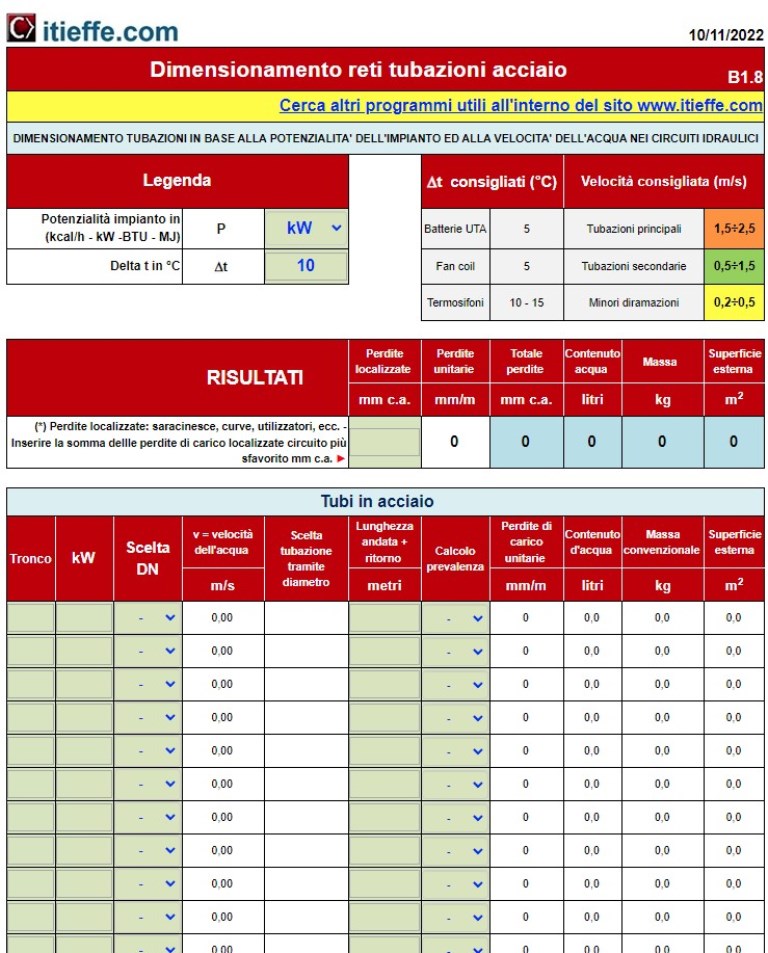
Steel
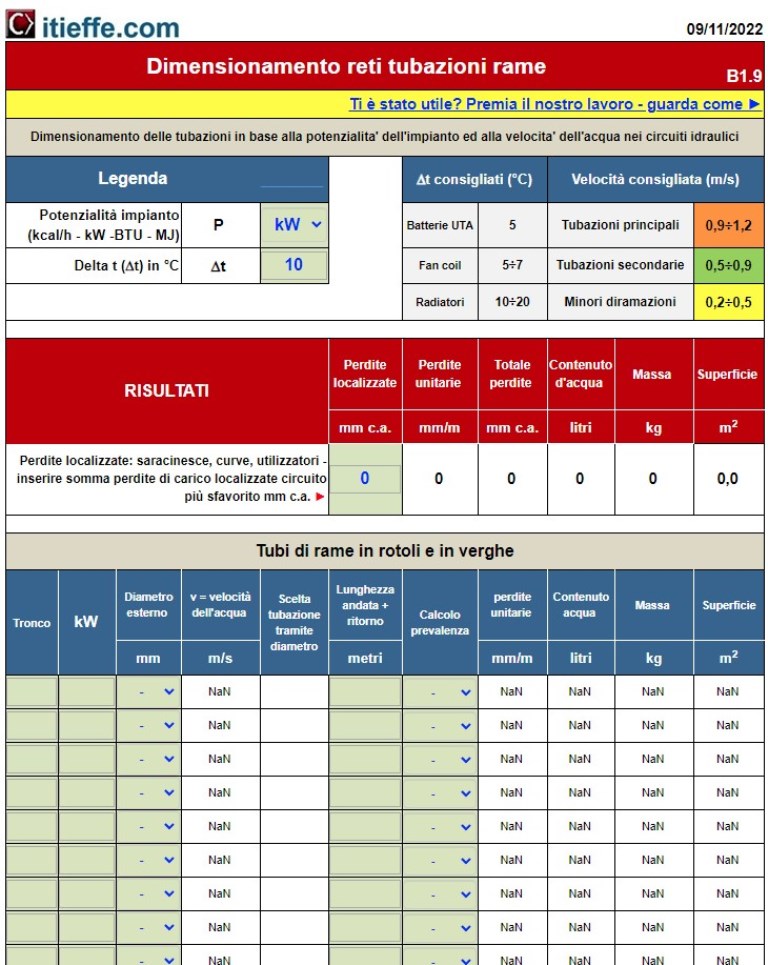
Copper
Note: the sum of the localized head losses must include losses other than those of the pipes (boiler, radiator, convector, curves, etc.). In practice, with a water speed of about 1,5 m/s, the value is of 335 mm approx per unit).
Terminal elements
They have the task of supplying the room to be heated with the thermal energy necessary to satisfy the thermal load.
In heating systems, the types of terminal elements are:
- radiators;
- fan coil;
- radiant panels.
- air heaters
Radiators
The most common terminal elements are radiators (also called: radiators). In most cases they are supplied with hot water at an inlet temperature of about 75 ÷ 85 ° C.
Radiators exchange heat mainly by radiation and to a lesser extent by convection.
They are classified according to the material they are made of: cast iron, steel and aluminum.
Fan coils
They consist of a metal casing containing a finned coil generally in copper-aluminum, a filter and a multi-speed fan. The fan coil can also be used for summer cooling.
Radiant panels

Made with very large surfaces that exchange heat by radiation.
The most common are radiant floor systems, with plastic pipes placed above a layer of insulating material and covered by the screed and the floor.
Air heaters
Consisting of batteries of finned tubes that can be powered by hot water or steam. They are crossed by air flows moved by fans and their characteristics are low cost and high noise. They are of high potential and suitable for industrial environments.
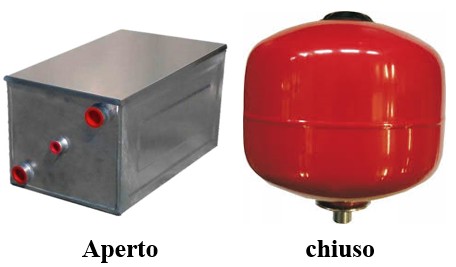
Expansion vessel
The expansion tank must be inserted in the hydraulic circuit of the hot water system. It is a device that serves to absorb the variation in water volume caused by the temperature increase, and allows the correct operation of a heating system in all its operating phases, avoiding overpressures that could damage the system itself.
The expansion vessels are divided into open and membrane vessels.
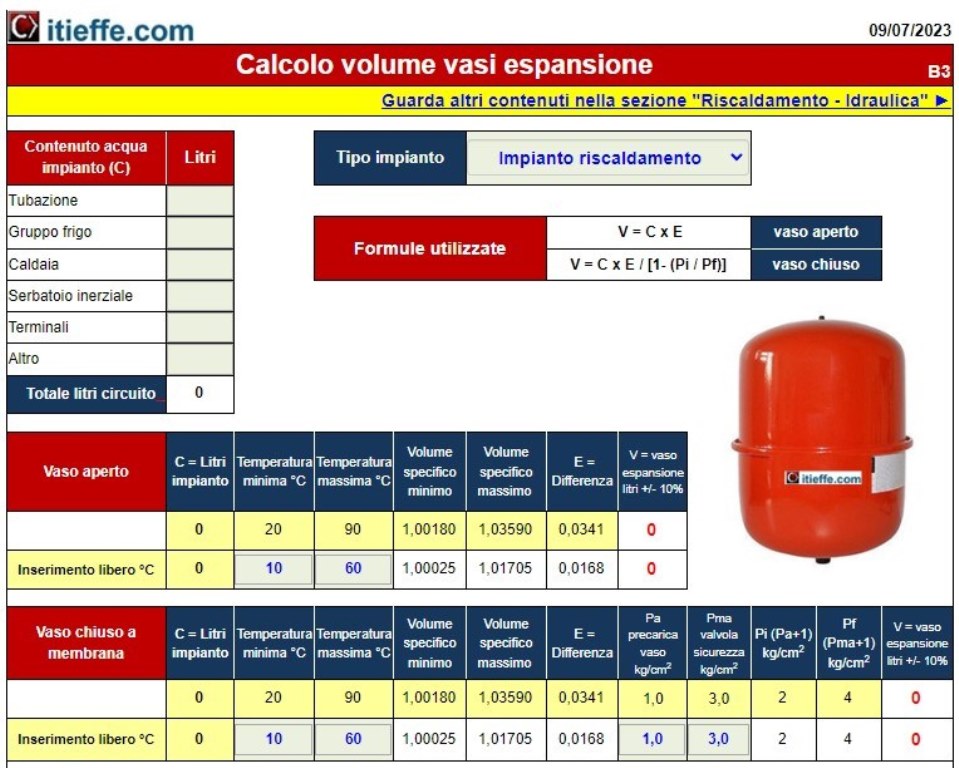
For their calculation it is necessary to know how much water volume is present in the system. It can be calculated by accessing the following program:
To calculate the expansion vessel both open and closed, access the following program:
Hot water delivery and return pipes

They are generally made of copper or steel
Copper has a marked maneuverability and workability (bending by hand) and the possibility of finding tubes with reduced diameters on the market. They are used almost exclusively where small piping diameters are required (less than 20 mm). The possibility of adapting the copper pipes to the needs of the building allows a reduction of special pieces. If necessary, there are copper and bronze fittings that can be soldered to copper by brazing.
For pipes with a diameter greater than 20 mm, steel is generally used, which makes it easier to create special pieces. Among the different types of steel, the seamless one is considered the best for plant engineering purposes. For curves, corners and junctions, special special pieces are on the market to be installed with threading or welding.
Their sizing is carried out using the programs already indicated above:
Sizing of pipe networks - steel
Sizing of copper piping networks
If you also want to calculate the weight. The water content and other parameters, please note that within the site www.itieffe.com there are dedicated programs:
Electric power and control panel
In small systems, it is replaced by a socket with plug (or double switch) and a thermostat that regulates the ambient temperature.
Conclusions
So let's recap, we have:
- took a look at the regulations in force;
- observed the scheme of a simple apartment plant;
- compared the various types of heating fuels through the program: "Heating fuel cost calculation";
- with the program "Heat requirement and radiators"Made the necessary calculations to trace the potential of the heat generator and radiators;
- seen how the circulation electric pumps are sized (Sizing of electric pumps);
- sized the pipes in copper o steel with the programsPiping sizing". With the same program, the head necessary for the circuit was calculated to reduce pressure drops;
- compared some of the types of terminals most used;
- calculated the amount of water present in the circuit with the program: "Calculation of system water volume";
- sizing the expansion vessel with the program: "Calculation of expansion vessel volume";
- observed the distribution networks, always considering that the following programs were used for their sizing: "Piping sizing"
- finally we saw how the boiler is electrically powered and how the temperature is regulated by inserting a thermostat in the room.
All the indications given in this paper can be of help to thermo technicians, installers and plumbing technicians but above all, they are published for information purposes for all those who intend to have a heating system built and first have a "smattering" of the material.
Good job everyone
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Heating - Plumbing
- Pipelines
- Heating tables
- pumps
- Heating drawing diagrams
- Domestic hot water
- Combustible gases