Energy labeling
This guide created by Itieffe represents an informative document of growing relevance in the current context, in which environmental awareness and energy efficiency have become global priorities. This paper aims to provide an in-depth understanding of energy labelling, a classification and communication system that informs consumers about the energy efficiency of electronic products and light sources.
In this introduction, we would like to highlight the importance of energy labeling as a key tool to promote the adoption of more energy efficient products. This initiative is crucial to reduce energy consumption, limit greenhouse gas emissions and save money for consumers, thus contributing to global efforts to address climate change and energy sustainability.
The main features and topics addressed in this paper include:
- Energy labeling definition: we will explain in detail what energy labeling is, how it works and which products are subject to this classification system.
- Benefits of energy labelling: we will discuss the benefits of energy labelling, including energy savings, reduced operational costs, informed consumer choice and positive impacts on the environment.
- Energy classification: we will describe the different energy rating categories used in labeling, such as A+++, A++, A+, A, B, C, D, etc., and what they represent in terms of energy efficiency.
- Label information: we will illustrate some details on the energy label, including technical data, estimated energy consumption, and other relevant information.
- Rules and regulations: We will explain the national and international laws and regulations governing energy labelling, promoting compliance and standardisation.
- Environmental and social impact: we will discuss the importance of energy labeling in reducing CO2 emissions and achieving energy sustainability goals.
The main objective of this paper is to provide a complete and accessible guide to energy labelling, educating readers on its importance and the useful information provided by energy labels. This tool is designed to guide consumers in choosing more efficient products and to encourage the production of increasingly energy-sustainable electronic devices and light sources.
Energy labeling
In the European Journal L315 of 5 December 2019, a series of regulations were published concerning the energy labeling of some electronic devices and light sources.
In particular, the following have been published:
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2013 of 11 March 2019 regarding the energy labeling of electronic displays;
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2014 of 11 March 2019 as regards the energy labeling of household washing machines and household washer-dryers;
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2015 of 11 March 2019 as regards the energy labeling of light sources;
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2016 of 11 March 2019 as regards the energy labeling of refrigerating appliances;
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2017 of 11 March 2019 regarding the energy labeling of dishwashers;
- Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2019/2018 of 11 March 2019 as regards the energy labeling of refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function.
Furthermore, the EU Regulations have been published which establish specifications for eco-design:
- refrigeration appliances;
- separate light sources and power supply units;
- electronic displays;
- dishwashers for domestic use;
- household washing machines and household washer-dryers;
- of refrigerating appliances with a direct sales function.
Comparison between old and new labeling scale (rescaling)
Standard energy labeling
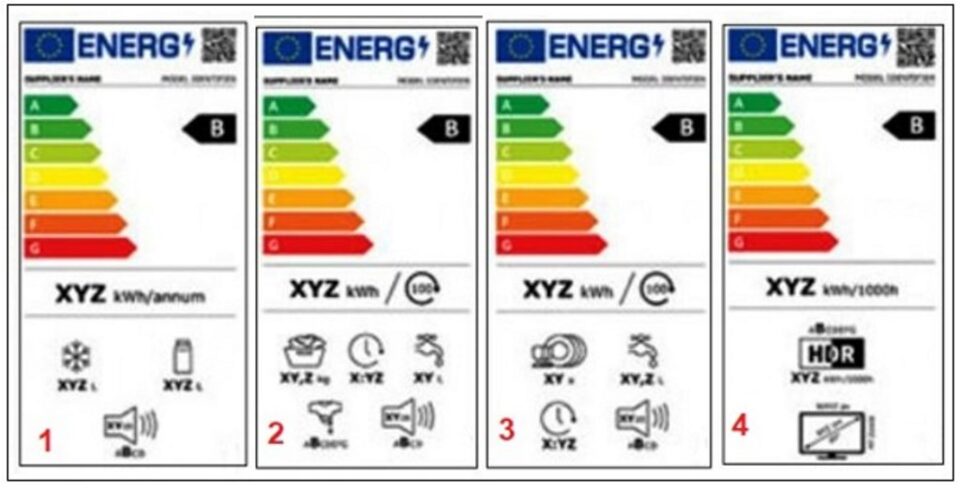
- refrigerators
- washing machines
- dishwasher
- televisions
Reference legislation
Regulation (EU) on energy labeling of light sources
The Delegated Regulation 2019/2015 integrates the regulation (EU) 2017/1369 of the European Parliament and of the Council with regard to the energy labeling of light sources and repeals the delegated regulation (EU) n. 874/2012 of the Commission.
The regulation establishes requirements for the labeling of light sources, with or without integrated control gear, as well as for the provision of additional information in this regard.
The requirements also apply to light sources placed on the market as part of a container product.
Standard size label for light sources
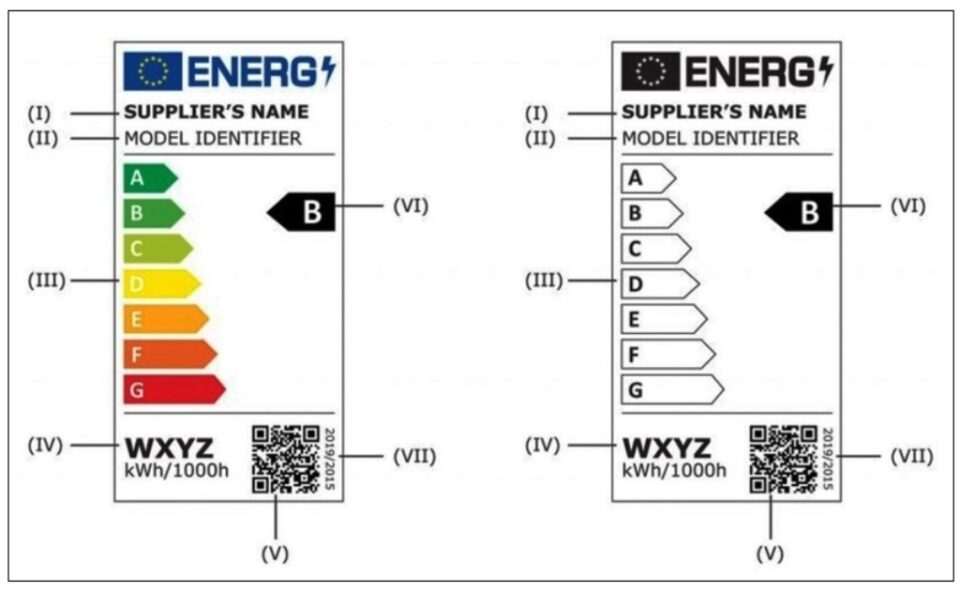
A light source label includes the following information:
- I – trademark or name of the supplier;
- II – vendor model identifier;
- III – scale of energy efficiency classes from A to G;
- IV – electricity consumption of the light source in on mode per 1 000 hours, expressed in kWh;
- V – QR code;
- VI – energy efficiency class according to Annex II;
- VII – number of this regulation, i.e. «2019/2015».
Obligations of suppliers
Light source suppliers shall ensure that:
- each light source placed on the market as a standalone product (i.e. not in a container product) in a package is accompanied by a label printed on the package;
- the parameters of the product information sheet, as set out in Annex V, are entered in the product database;
- at the specific request of the distributor, the product information sheet is made available in printed format;
- the content of the technical documentation referred to in Annex VI is entered in the product database;
- visual advertisements relating to a given light source model display the energy efficiency class of the model and the range of energy efficiency classes appearing on the label, in accordance with Annexes VII and VIII;
- technical promotional material describing the specific technical parameters of a given light source model, including technical promotional material on the Internet, includes the energy efficiency class of the model and the range of energy efficiency classes shown on the label, in accordance in Annex VII;
- an electronic label in the format and containing the information set out in Annex III is made available to distributors for each light source model;
- an electronic product information sheet as set out in Annex V is made available to dealers for each light source model;
- at the request of the distributor and in accordance with Article 4(e), printed labels for rescaling (scale adjustment) of products are supplied in the form of a sticker having the same dimensions as the existing label.
What changes in the Energy class appliances 2021
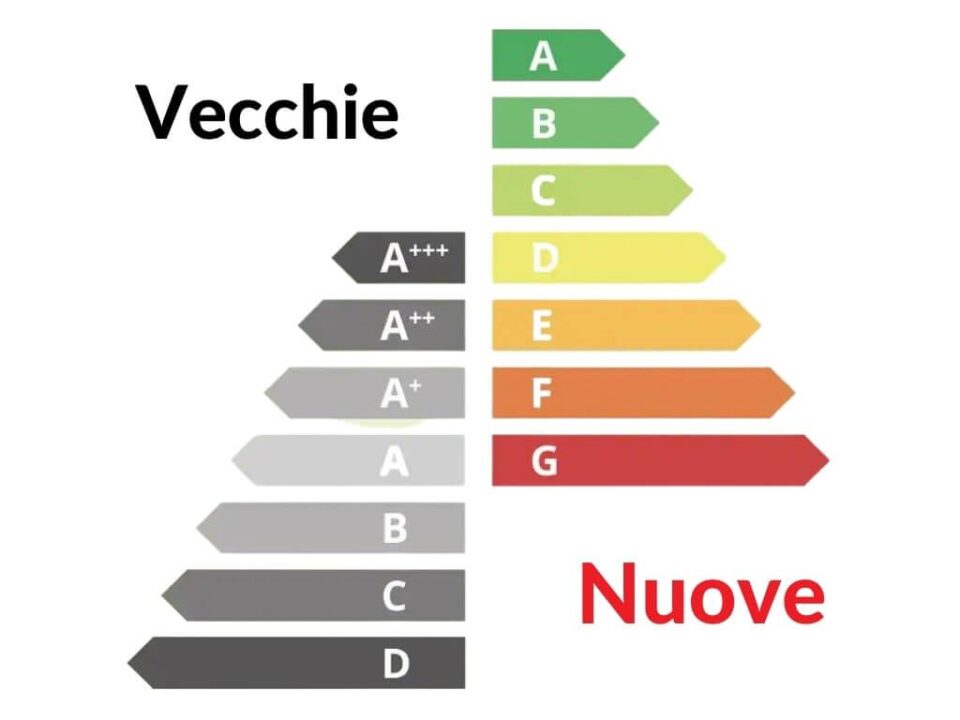
The old generation energy labels were introduced by the European Community in 1995. They were based on a classification that ranged from the letter A to the letter D. Subsequently, to indicate a lower energy consumption in class A, the symbols began to be added “+”, “++”, “+++”. This nomenclature, however, has not demonstrated its communicative effectiveness, remaining obscure for the consumer. For this reason, the European Community wanted to introduce the new 2021 energy label.
Since most of the household appliances on the market belong to classes ranging from A+++ to B (showing in this a particular attention of manufacturers to the environment), the EC has decided to rescale the old labels with a nomenclature ranging from A to G The first big change, at the label level, is therefore the disappearance of the + symbol. This provision is included in the European Regulation 2017/1369. Instead of the A with the "+" symbol, there will be a scale from A to G, in which the A will be bright green and will indicate the maximum energy efficiency, and the G will be red and will indicate the least efficient class.
Furthermore, it is expected that from 2024 class G and class F appliances will disappear from the market. In addition to the energy scale, the label also shows the annual energy consumption, measured in kWh, the consumption for 1.000 hours or 100 cycles, always returned in kWh and the QR code. It refers to the European database from which it is possible to download the technical data sheet of the product. The European Regulation, in force since 1 March 2021, provides for the application of the new energy labels for refrigerators and freezers, TVs, washing machines, washer dryers and dishwashers. Starting from 1 September 2021 also for light sources and all other products will follow in 2022.
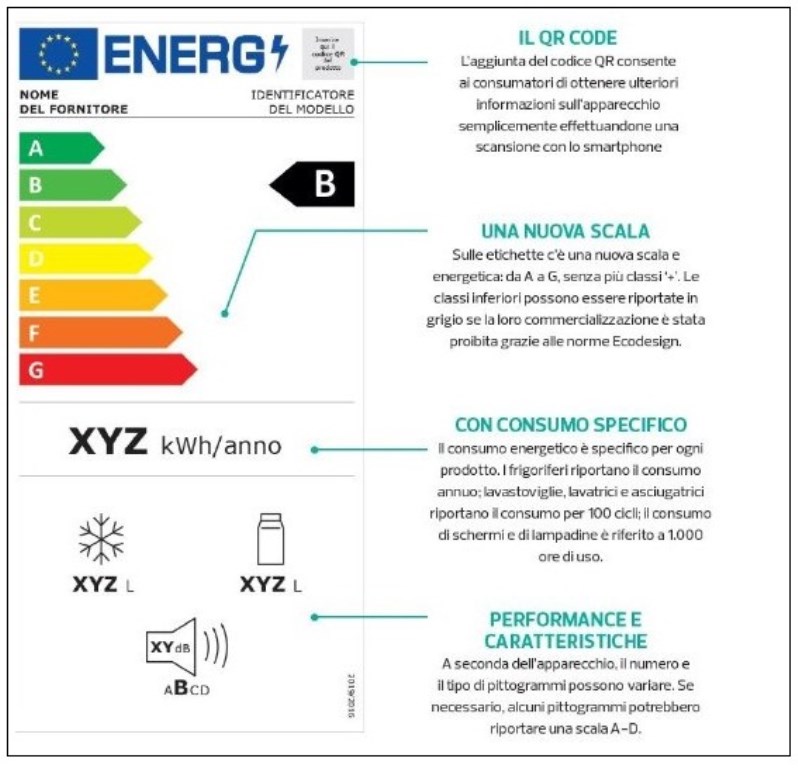
New energy label: elements that characterize it
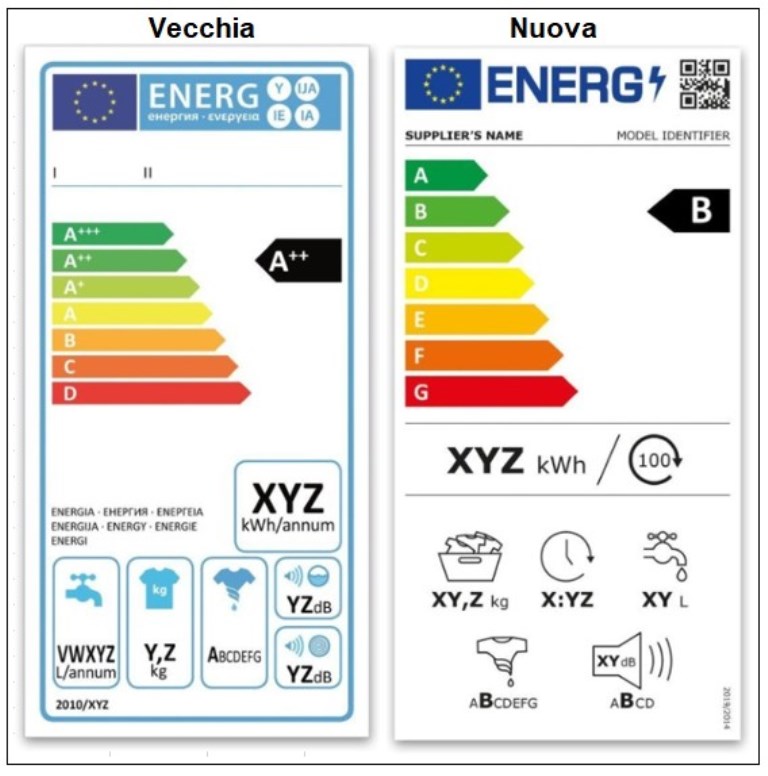
The new energy labels for appliances introduced in 2021 can be divided into areas. Each area corresponds to precise information that the manufacturer wants to provide. Inside the label we find:
- At the top, the flag of the European Community, with the wording Energy which identifies the label.
- Next to the word Energy, the QR code of the appliance.
- Immediately after the name of the brand and the identification name of the model.
- The scale of the new energy classes, which express their efficiency and range from A to G. It can also show the old nomenclature to allow the comparison between old and new energy classes of household appliances.
- It will distinguish smart appliances with the “smart” icon.
Below the scale there are pictograms which indicate the energy consumption during use of the ECO program expressed in kWh per 100 cycles; the capacity of the ECO programme; the water consumption expressed in liters for each cycle carried out with the ECO programme; the duration in hours and minutes of the ECO program; the noise level expressed in dB and the respective class it belongs to; compliance with the European regulation 2019/2017.
The new energy classes
Energy classes A, B, C
The energy classes A, B and C are the classes that identify appliances equipped with cutting-edge technologies, with low energy consumption and greater savings on bills. These new energy classes of household appliances are expressed in dark green for the letter A, light green for B and lime green for class C. There are currently very few household appliances that reach the highest classes, so efficiency is high energy required. There are only a few smart appliances on the market, such as washing machines and dishwashers, which fall into higher energy classes. Maximum energy efficiency is obtained from a class A household appliance and these are the appliances consumers will aim for to obtain maximum savings and sustainability.
Energy class D
In the energy label, energy class D is expressed in light yellow. This class corresponds in the new energy label to the old class A+++. We are therefore speaking of appliances with excellent performance in terms of efficiency and consumption, but also of appliances belonging to the best old generation energy class.
Energy class E
The energy label presents the energy class E in the color light orange. In comparing old and new energy classes of household appliances, class E corresponds to the old class A++, therefore it belongs to a wide range of household appliances that populate our homes and are considered very efficient with good energy savings.
The energy class F
Energy class F is represented in dark orange, almost brick. In the energy label it corresponds to the bar above the letter G. Obviously, energy class F is also considered a low energy saving class, even if it corresponds to class A+ in the old nomenclature.
The energy class G
For energy efficiency, the energy class G is in last place and its red bar at the base of the scale indicates, according to the new parameters, a class that has a high energy consumption, even if the corresponding appliances could fall into this group to the old class A. Therefore, one of the appliances, not entirely ecological but which until recently belonged to a higher class, is now considered a less performing energy class product.
