Failures of refrigeration circuits
Analysis of the most frequent malfunctions of the refrigeration circuits and suggested ways of intervention
This guide, designed and created by Itieffe, represents a good resource for operators, engineers and technicians who work with refrigeration systems and refrigeration systems. This guide has been designed to address a wide range of issues and faults that can occur in refrigeration circuits, providing a detailed overview of the underlying causes and strategies for diagnosing and resolving such issues. Before examining the specific content of the guide, it is important to provide a background to understand the context and importance of this resource.
Context of the Use of Refrigeration Circuits:
Refrigeration circuits are essential components in a number of applications, from food and drug storage to building air conditioning and industrial applications. Their reliability is essential to ensure that these systems function correctly, maintaining the quality of the products and the comfort of the users.
Faults and Breakdowns in Refrigeration Circuits:
During their life cycle, refrigeration circuits can be subject to a series of faults and failures that can compromise their operation. These failures can include refrigerant leaks, compressor malfunctions, expansion problems, and many others. Identifying and resolving these issues early is crucial to ensuring reliable operation and good energy efficiency of refrigeration systems.
Importance of the Guide:
This guide is important for several reasons:
- Problem solving: provides a detailed guide to promptly identify the causes of faults and failures in the refrigeration circuits and offers practical advice on how to resolve them.
- Energy efficiency: helps improve the energy efficiency of refrigeration systems, helping to reduce operating costs and environmental impact because if a refrigerator works well, its performance will be maximum.
- Safety: helps prevent dangerous situations related to refrigerant leaks or system malfunctions.
- Extended operating life: allows you to extend the operating life of the refrigeration circuits, reducing the need for expensive replacements.
- Regulatory compliance: Helps ensure that refrigeration systems comply with applicable laws and regulations.
Contents of the Guide:
The guide is designed to be a practical and informative resource. The “Synoptic Model” vision makes it clear and accessible to all. Its content may include:
- An overview of the main types of faults and failures that can occur in refrigeration circuits.
- Detailed explanations of the underlying causes of each problem.
- Diagnosis tips and steps to follow to resolve faults effectively.
- Practical examples and case studies to illustrate the application of the proposed resolution methods.
In conclusion, this guide is an effective tool for ensuring the correct operation and maintenance of refrigeration systems in a wide range of applications. Its adoption helps preserve the reliability of refrigeration circuits, the safety of operators and the quality of refrigerated products.
Failures of refrigeration circuits
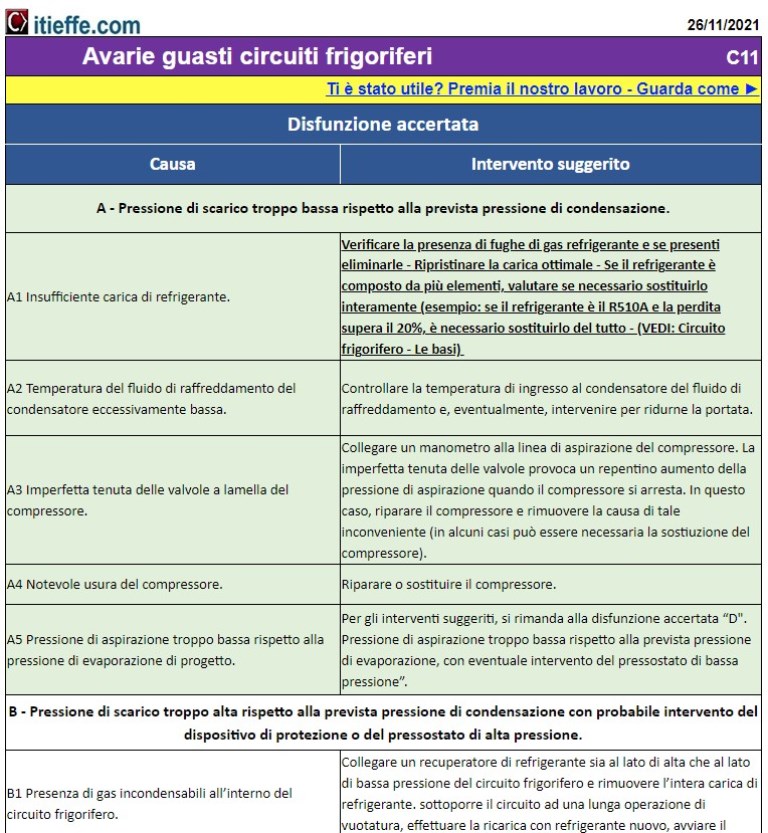
Knowing how to eliminate the problems that arise in a system is not easy, we will certainly say that it is relatively easy, because the first thing that is required of the refrigeration technician is the perfect knowledge of the cycle and of the work that must be done by each single mechanical and electrical organ of the system (See: Refrigeration circuit - The basics).
A good refrigeration technician must have knowledge of hydraulics, heat, electricity, mechanics, know how to weld and why not, chemistry. The refrigeration technician is a complete professional who embraces various sectors.
Nowadays the plumbers who install autonomous air conditioning systems (split system) consider themselves “refrigerators”; it is not like that and if it does not progress otherwise, it will never be like this. The refrigeration technician does it only those who are refrigeration technicians It is a profession that evolves day by day and every day gives you the opportunity to learn something.
This paper gives the first general indications of how to carry out the analysis of the most frequent refrigeration circuit malfunctions and the suggested intervention methods. A second, more detailed part will follow for the "Drawbacks of running refrigerators".
Let's also analyze the safety regulations that intervene in these cases
SAFETY RULES
- this equipment is intended exclusively for professionally trained operators who must know the fundamentals of refrigeration, refrigeration systems, refrigerant gases and any damage that can cause equipment under pressure.
- carefully read the manuals of the manufacturers, the scrupulous observance of the procedures illustrated is an essential condition for the safety of the operator, the integrity of the equipment and the consistency of the declared performances.
- the compressor must only work with refrigerant fluids indicated by the manufacturer.
- during the various operations, absolutely avoid dispersing the refrigerant in the environment; this precaution, in addition to being required by international environmental protection standards, is essential in order to avoid that the presence of refrigerant in the environment makes it difficult to locate any leaks.
- do not tamper with or modify the calibration of the safety and control systems.
- in no case introducing oxygen inside the compressor can cause an explosion.
- check that the characteristics of the power supply network are adequate for the characteristics of the compressor.
- before powering up the compressor, check that the suction and compression cocks are completely open and that the terminal box cover has been sealed.
- always check that the compressor is connected to an adequately protected power supply network equipped with an efficient earth line.
- remove the terminal box cover only after cutting off the power supply to the compressor.
- do not start the compressor when there are high vacuum conditions inside.
- avoid inhaling refrigerant vapors.
- it is advisable to wear adequate protection such as goggles and gloves; the low boiling temperature of the refrigerant can cause physical harm to the operator.
- avoid contact between the refrigerant and open flames or hot surfaces; at high temperatures, the refrigerant decomposes releasing toxic substances, harmful to both the environment and the operator.
- the compressor is supplied with a nitrogen holding charge at a pressure of 1 bar; remove the compressor bolts only after removing the holding charge.
- touch the compressor only after a long period of inactivity; during operation, some of its parts can reach temperatures above 100 ° C and take time to cool down.
- always use common sense.
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
Failures of refrigeration circuits
The program / paper shown below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE
