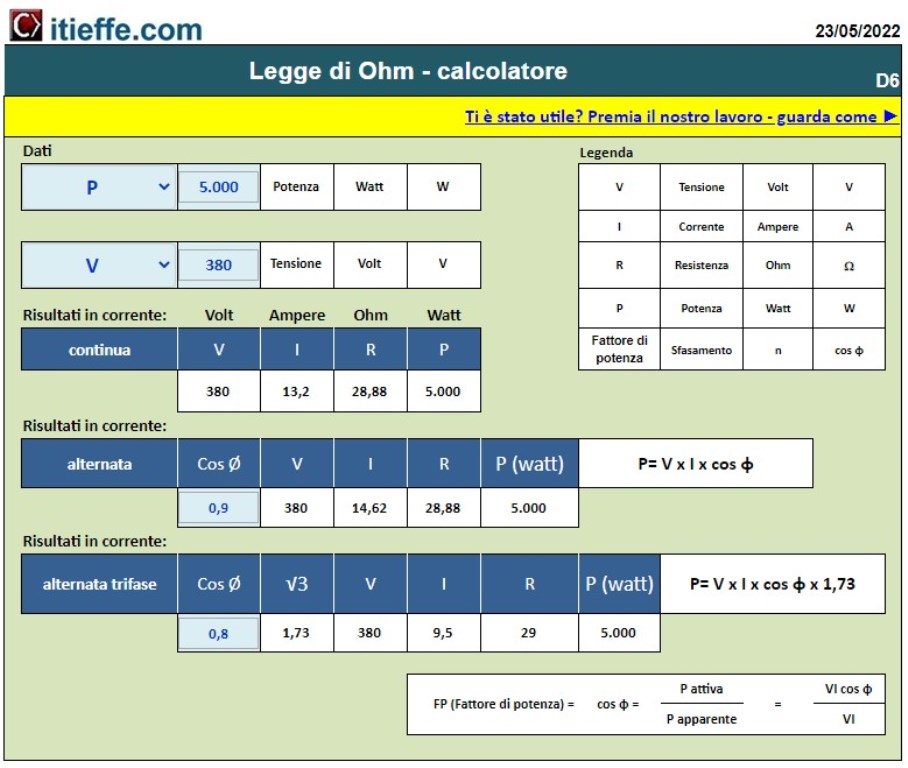
Knowing only two data it is possible to trace all the others involved in Ohm's law (voltage, current intensity, resistance and power). Results in alternating and three-phase alternating current are also reported – Characteristic values of cos φ are also indicated
Welcome to the program offered by Itieffe "Ohm's Law - Calculator". In an increasingly interconnected and technology-dependent world, understanding the fundamental principles of electricity and electronics has become essential for everyone. Ohm's law, enunciated by the German physicist Georg Simon Ohm, represents one of these fundamental pillars on which much of our modern society is based.
Why this program
This program was created with the aim of making Ohm's Law accessible and understandable to everyone, from beginners to electronics enthusiasts. Whether you're a student just starting to explore the world of electricity, a hobbyist curious to understand how electrical circuits work, or a professional who needs to make quick and accurate calculations, this program is designed for you.
Through an intuitive and easy to use interface, you can enter the values of the quantities involved in a circuit (power, voltage, current, resistance and phase shift) and instantly obtain the results of the calculations, saving precious time and reducing the possibility of errors. In addition, the program provides clear and concise explanations of the concepts involved to ensure a thorough understanding of Ohm's Law.
We are thrilled to introduce you to the Ohm's Law Calculator program and to be by your side as you explore the wonders of electronics. Whether you're looking to solve complex problems or just refresh your knowledge, this tool will be your reliable companion. We are confident that you will master Ohm's Law and apply it creatively and effectively.
We are grateful to take you on this journey through electrical circuits and are confident that the program will help illuminate your understanding of electricity. Good calculation with Ohm's Law.
Ohm's law - calculator
Knowing only two data, it is possible to trace all the others affected by Ohm's law (voltage, current intensity, resistance and power).
The results are shown in direct, alternating and three-phase alternating current.
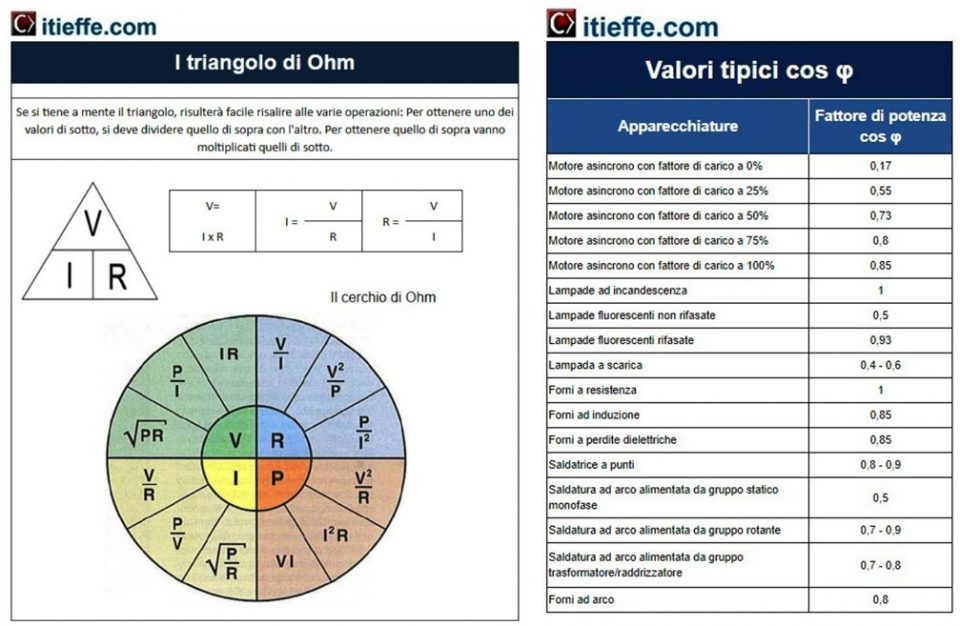
In addition to the Ohm triangle, the characteristic values of cos φ are indicated
Ohm's law is a mathematical formula that describes the correlation of electrical quantities (resistance, current, voltage) as they vary.
By resistance (R) we mean the obstacle that the current encounters in its path, the higher it is, the more difficult it will be for the current to cross it; its unit of measure in the SI (international system) is the ohm, represented by the Greek letter omega (Ω).
By current (I), expressed in amperes, we mean the quantity of electrical charges that pass through a conductor in the unit of time.
By voltage (V) instead we mean the potential difference of one point with respect to another expressed in volts.
Clearly, the higher the obstacle, the lower the intensity of current that passes through it, it is therefore clear that, with the same ddp (potential difference) applied, the current is inversely proportional to the resistance.
For the voltage, on the other hand, the higher it is, the greater its attraction force which it generates to move the electric charges, consequently for the same resistive value it will be directly proportional to the current intensity.
The name is due to the German physicist Georg Ohm, who, in a treatise published in 1827, described the measurement of current and potential difference through simple circuits with wires of different lengths, even if the original formulation is more complex than the current form .
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Electricity - Electronics
- Calculation of color coded electric resistances
- Electric - electronic tables
- Electrical drawing diagrams
Ohm's law - calculator
The program below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE



