Specific weight various materials
This paper created by Itieffe is a document that aims to explore the concept of PS in detail and provide detailed information on a wide range of materials. This topic is of fundamental importance in various scientific, engineering and industrial fields, since weight is a fundamental characteristic of materials and influences numerous aspects of practical applications.
In this paper, we will examine the following key points:
- Definition: we will explain the concept of specific weight as the density of a material, that is, the amount of mass contained in a specific unit of volume. We will use common units of measurement, such as kilogram per cubic meter (kg/m³) in the International System (SI).
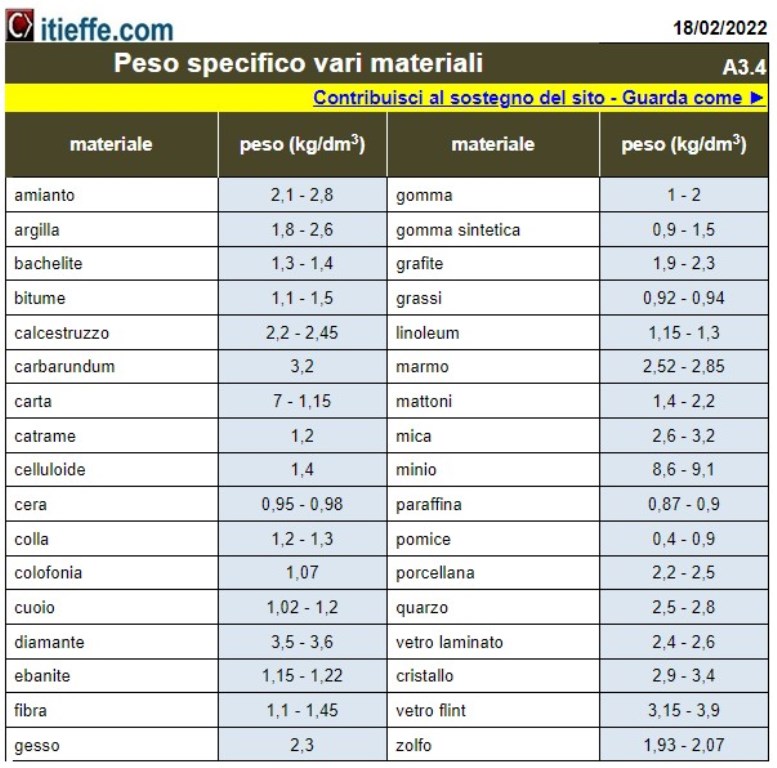
- Common Materials: we will explore the weight of a wide range of common materials. Specific data will be provided on each material.
The main objective of this paper is to provide a comprehensive information resource for anyone interested in the weight of materials. Understanding this concept is critical for a wide range of professionals, including engineers, architects, materials scientists, and designers, as it impacts material selection, structural design, and practical applications in numerous industries.
Specific weight various materials
Also known as density, it is a physical quantity that represents the amount of mass of a substance contained in a given unit of volume. In other words, it provides a measure of how much matter is concentrated in a specific space. It is usually expressed in units of mass per unit of volume, such as kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) in the International System (SI).
The general formula for calculating specific gravity is:
Specific Weight=Mass/Volume.
Where:
- “Mass” represents the amount of matter contained in the object or substance, usually measured in kilograms (kg).
- “Volume” indicates the space occupied by that mass, usually measured in cubic meters (m³).
Specific gravity can vary greatly between different substances and materials. For example, the specific weight of water is approximately 1000 kg/m³ at room temperature. This means that one cubic meter of water has a mass of 1000 kilograms. Denser materials, such as iron, will have a much higher specific gravity, while less dense materials, such as air, will have a much lower specific gravity.
Knowledge of specific gravity is fundamental in several scientific and engineering disciplines, as it affects various aspects, including the load-bearing capacity of structures and the choice of materials in specific applications.
Specific weight various materials
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
Specific weight various materials
The program below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE
