Calculation of the volume in liters of open and membrane expansion tanks - cold and sanitary water systems
Welcome to our innovative expansion vessel volume calculation program. This tool was created by Itieffe to help engineers, designers and professionals in the thermo-hydraulic sector in carrying out precise and rapid calculations relating to the sizing of the expansion vessels necessary for heating systems.
expansion vessels
Expansion vessels play a fundamental role in thermal systems, allowing the volume of heat transfer fluid to vary in response to variations in temperature and pressure, thus ensuring the correct functioning and efficiency of the systems.
This program was developed and made available free of charge, taking into account the latest formulas and industry standards, in order to provide accurate and reliable results.
optimal volume of the expansion vessels
Whether you are involved in the design of complex heating systems or are simply interested in accurate calculations for maintenance purposes, our tool will support you in determining the optimal volume of expansion vessels needed for your system.
We invite you to use the “Expansion vessel volume calculation” program to simplify your daily activities, reducing the margin of error in calculations and saving precious time.
Remember that correct sizing of expansion vessels not only improves the safety and energy efficiency of the system, but also contributes to its overall lifespan.
We are confident that this tool will become an essential ally in your work. Thank you for choosing our program and good luck calculating the volume of the expansion vessels.
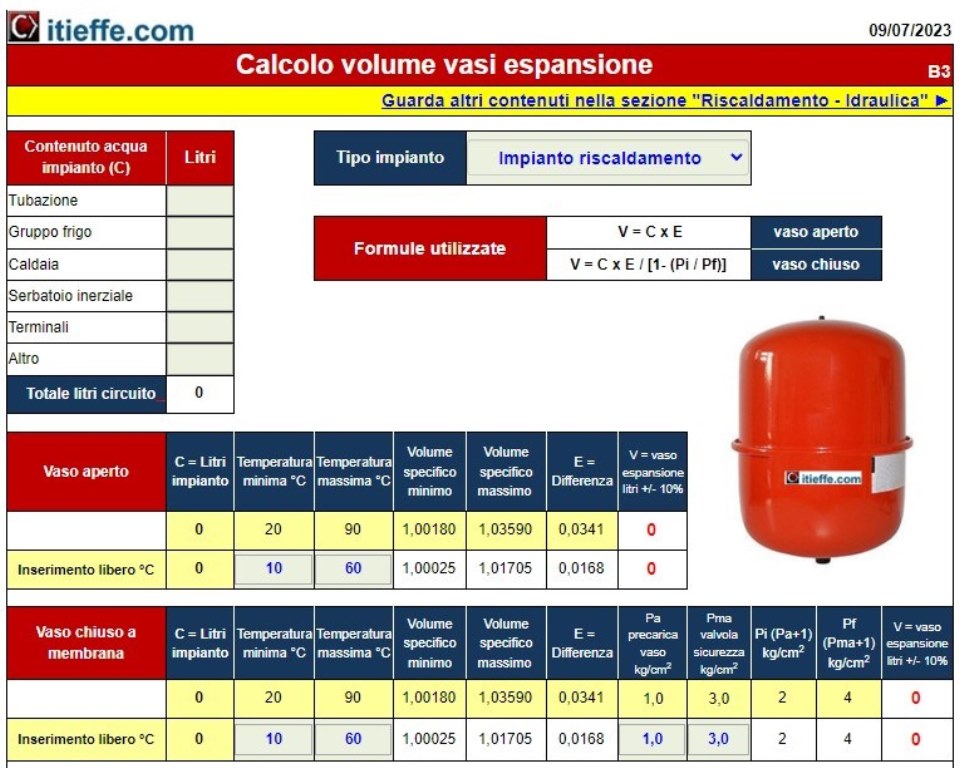
Calculation of expansion vessel volume
Simple program to calculate the volume in liters of open and membrane expansion vessels.
It can be applied to different types of systems: hot water, cold water and sanitary water heating.
let's analyze the program
Enter the total volume of water that is assumed to be contained in the "System water content" field. The volume is given by all the pipes, the content of the boiler or water cooler, the content of the terminals (radiators - panels - other).
In case of difficulty, you can use the program: "Calculation of system water volume”Which, in principle, gives quite precise indications.
Indicate the type of system being analyzed by choosing from the drop-down menu.
Enter the temperature values that are deemed necessary, comparing them with those indicated automatically.
Pi = absolute pressure in kg / cmq at which the gas cushion is preloaded, a pressure that cannot be lower than the hydrostatic pressure at the point where the vessel is installed (absolute pressure = gas pre-charge + 1). It is the absolute minimum pressure expressed in bars that we want to have in the system at the height of the vessel itself (absolute pressure = atmospheric pressure + 1).
It must be compatible with the requirements of the boiler manufacturer and with the total height of the system with respect to the installation point of the vessel.
For example, if the system extends three floors above the installation point of the vessel, we can roughly establish that it takes at least 9 m of approx to be sure that the water is present at least up to 9 m in height. For safety, we will establish a pressure of approx. 12 m (therefore about 1,3 bar) to be entered in the "Pi" field
Pf = absolute maximum operating pressure at which the safety valve is calibrated, in kg / cm², decreased by a quantity corresponding to the difference in height existing between the vessel and the safety valve if the latter is placed lower or increased if placed higher (Press. of plate + 1).
We will set the maximum final pressure (absolute pressure = maximum pressure + 1) that we want to have when the system reaches the maximum temperature (therefore in conditions of maximum expansion).
The safety valve in domestic boilers is usually set at 2.5 - 3 bar, but it is advisable to keep within a suitable safety margin (we recommend a value between 1,7 and 2 bar).
Instructions
How to proceed
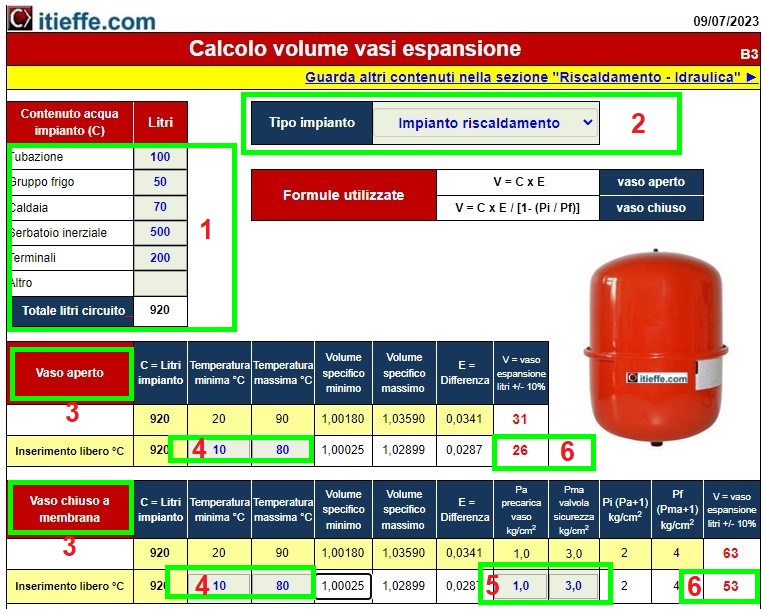
1 - Let's start calculating the water inside the system (also with the help of the programs indicated in the related links) and let's assume that it is 920 liters.
2 – we choose the type of system (DHW storage – heating – chilled water), which only provides the standard indication of the temperatures to be used for the water and does not affect the calculations. In our case: Heating system.
3 – choose for which type of expansion vessel the calculation will be made (open or closed), in our example we consider the data provided for the vessel closed with a membrane.
4 - in the line "free insertion" we indicate the minimum and maximum temperature in degrees centigrade that the water will have (in our case 10 and 80 ° C).
5 – insert the vessel preload values and the calibration pressure of the safety valve in kg/cm² (those placed in the upper row are indicative) analyzing what was said in the previous paragraph.
6 - let's observe the results - in our case we need a 53 liter jar.
Easy right?
good job
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
- Heating - Plumbing
- Pipelines
- Heating tables
- pumps
- Heating drawing diagrams
- Domestic hot water
- Combustible gases
Calculation of expansion vessel volume
The program below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE

