General indications of refrigerant gas
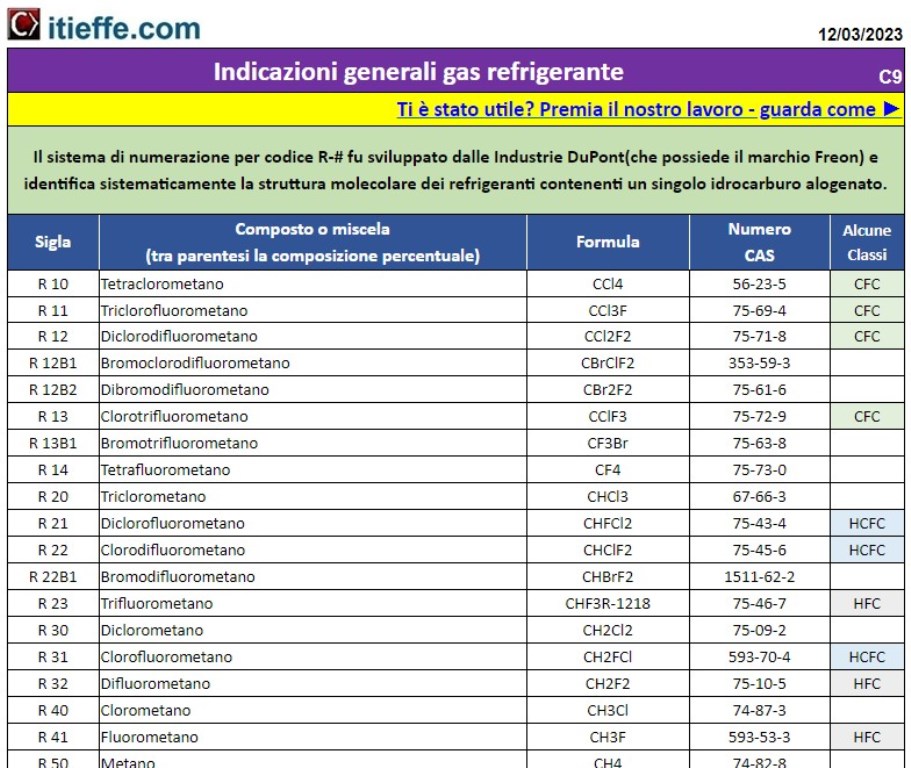
General indications on refrigerant gases - extended list - chemical compounds - formulas - CAS number - safety classes - illustrative table with the main characteristics
Itieffe is pleased to present this guide on "General Indications on Refrigerant Gases". This document was created by Itieffe to provide a broad overview of refrigerant gases used in a wide range of applications, from air conditioning equipment to industrial refrigeration systems.
Refrigerant gases play a crucial role in the refrigeration cycle, enabling cooling and air conditioning in residential, commercial and industrial environments. This guide is designed to be a comprehensive resource for anyone dealing with these types of gases, including HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning) professionals, refrigeration technicians, technicians, engineers and researchers.
Throughout this guide, we will explore the following key topics in detail:
- Introduction to refrigerant gases: we will provide a general overview of refrigerant gases, explaining their role in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
- Extended list of chemical compounds: We will present an extensive list of commonly used refrigerant gases, along with their chemical formulas, CAS (Chemical Abstracts Service) numbers and safety classes.
- Security classes: We will discuss the safety classes of refrigerant gases, which are critical to the safe handling of these chemicals.
- Illustrative table: we will provide a complete illustrative table with the main characteristics of refrigerant gases, facilitating consultation and comparison between the different compounds.
The reason for this guide
This guide is designed to be an informational and educational resource, ideal for those who want to learn more about refrigerant gases and for those who work in the HVAC, refrigeration or related industries. Understanding the characteristics, properties and classifications of refrigerant gases is critical to the safe and efficient design, installation and maintenance of refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
We hope this guide proves useful and informative, helping you navigate through the complex world of refrigerant gases and make informed decisions in your professional endeavors or personal projects.
General indications of refrigerant gas
General indications on refrigerant gases - extended list - chemical compounds - formulas - CAS number - safety classes - illustrative table with the main characteristics
CAS number (CAS Registry Numbers®)
What is a CAS number?
CAS Registry Numbers® or CASRN®, commonly referred to as CAS numbers, are unique numerical identifiers assigned to chemicals by the Chemicals Abstract Service (CAS: A Division of The American Chemical Society). CAS numbers provide a simple, consistent and reliable way to identify chemicals so they are recognizable regardless of your region.
Each CAS number is assigned to only one substance, ensuring that the CAS number is unique for that chemical. The number, which is assigned as soon as the chemical enters the CAS Registry® database, can be up to ten digits long and is separated into three parts by dashes. The first part contains two to seven digits, the second contains two digits, and the third part consists of a single digit, known as the check digit. In their current format, a maximum of one billion unique CAS numbers are available. They have no real chemical significance and are assigned in sequential order, so that newer substances have higher numbers than chemicals that previously entered the registry.
Example:
Sigla |
Compound or blend |
Formula |
CAS number |
| R10 | Tetrachloromethane | CCl4 | 56-23-5 |
Security classes
Table of the safety classes of refrigerants according to ISO 817
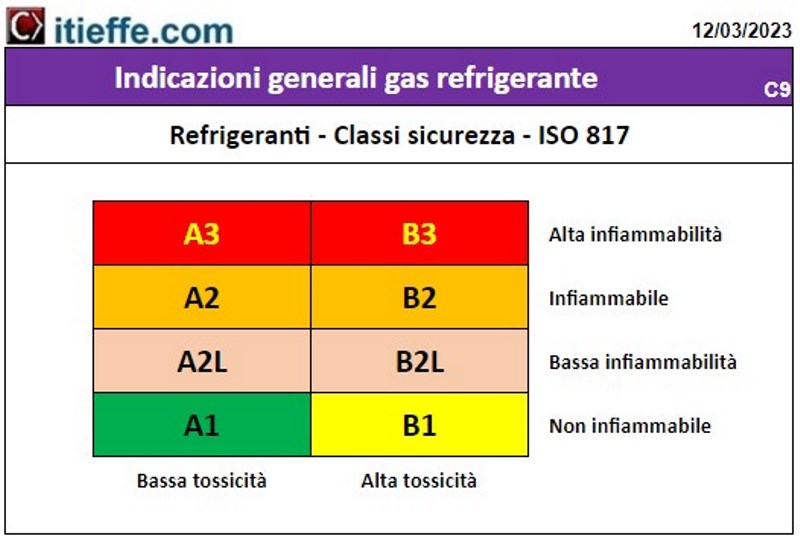
safety classification
ASHRAE defines it by using two alphanumeric symbols:
- a literal symbol regarding toxicity
- a numerical symbol regarding flammability
Toxicity
Regarding toxicity, refrigerants are divided into two groups:
- group A: this group includes all the refrigerants that are not toxic for concentrations equal to or lower than 400 ppm
- group B: this group includes all refrigerants that are toxic for concentrations below 400 ppm
Flammability
Regarding flammability, there are three main classes:
a) class 1: all refrigerants that do not present flame propagation in air at a temperature of 60 °C and at atmospheric pressure belong to this group;
b) class 2: all moderately flammable refrigerants that have a lower flammability limit greater than 0,10 kg/m belong to this group3 at a temperature of 60 ° C and atmospheric pressure and a combustion heat lower than 19000 kJ / kg;
c) class 3: all highly flammable refrigerants which have a lower flammability limit less than or equal to 0,10 kg/m belong to this group3 to the temperature 60 ° C and at atmospheric pressure or a heat of combustion greater than or equal to 19000 kJ / kg.
To adapt to the needs induced by the creation of new refrigerants of a chemical nature, ASHRAE, following the example of the ISO standards, has defined a sub-class, the 2L, which indicates those refrigerants that are slightly flammable such as, for example, the HFOs,R32 or ammonia. Sub-class 2L includes all class 2 refrigerants which have a flame propagation rate of less than 10 cm / s.
Safety of mixtures
Azeotrope and zeotrope mixtures can change their toxicity and flammability characteristics based on their composition, which can vary in the event of fractionation (for example in the case of a leak from a refrigeration circuit).
For this reason, each mixture is classified, both as regards toxicity and flammability, on the basis of the most dangerous fractionation situation that can occur.
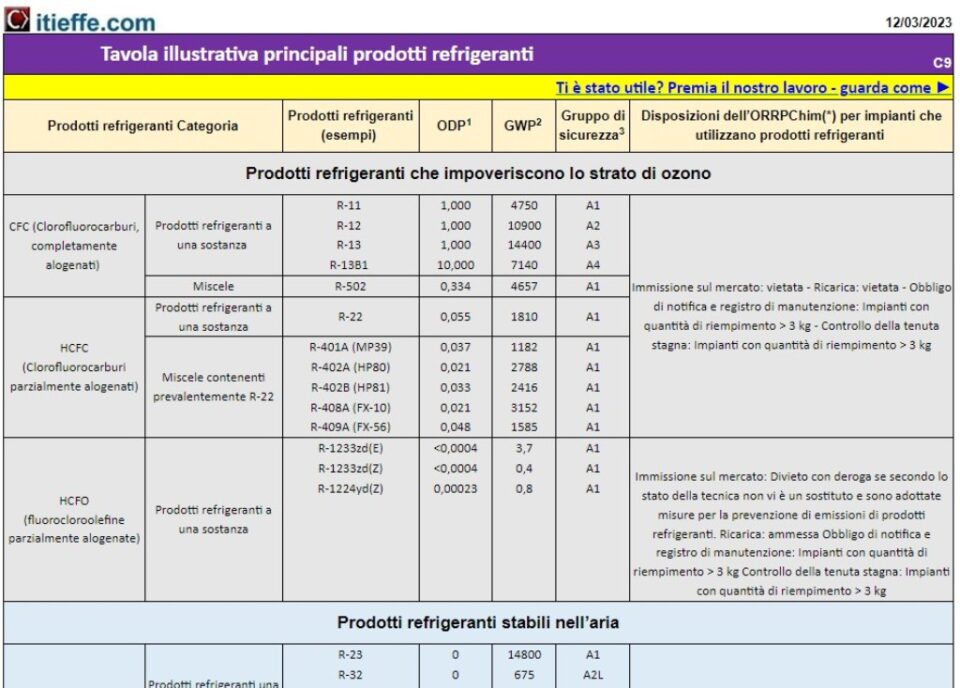
Illustrative table of the main refrigerant products
Other free programs of the same kind offered by itieffe ▼
General indications of refrigerant gas
The program / paper shown below is free to use.
To access the reserved version (see below), full page and without advertising, you must be registered.
You can register now by clicking HERE
